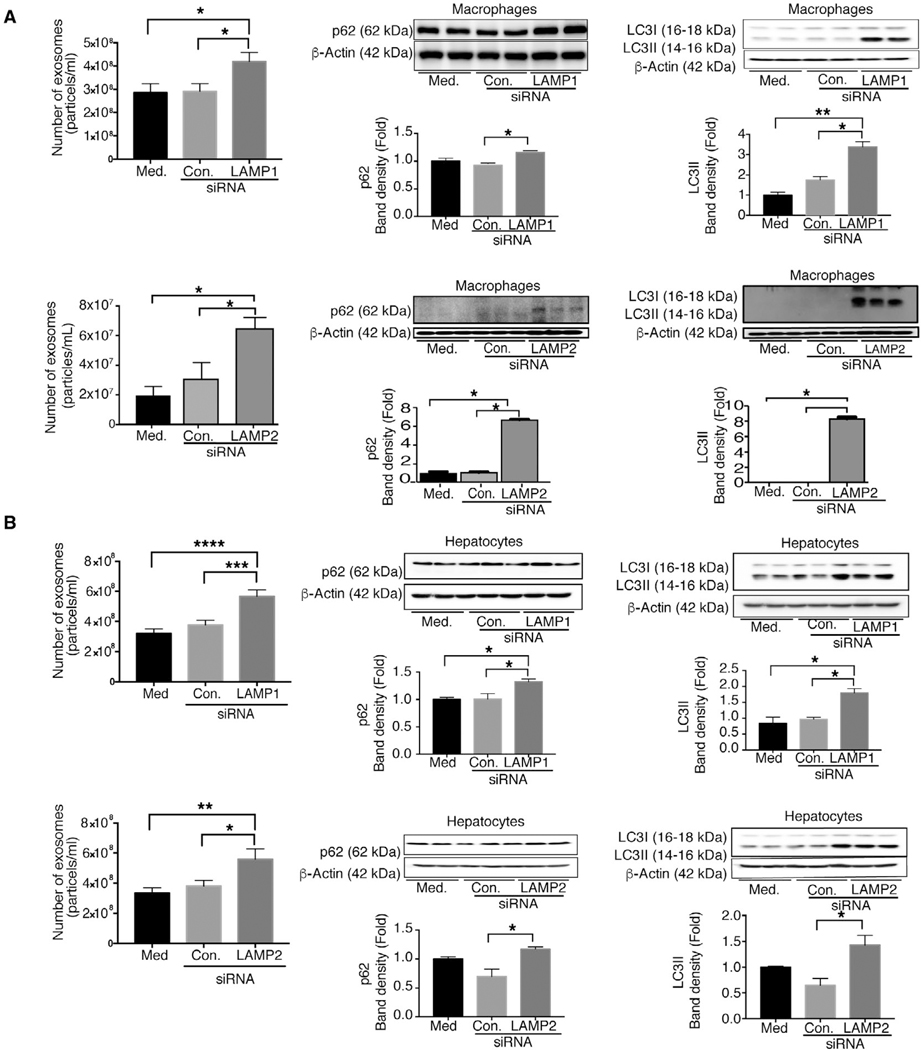
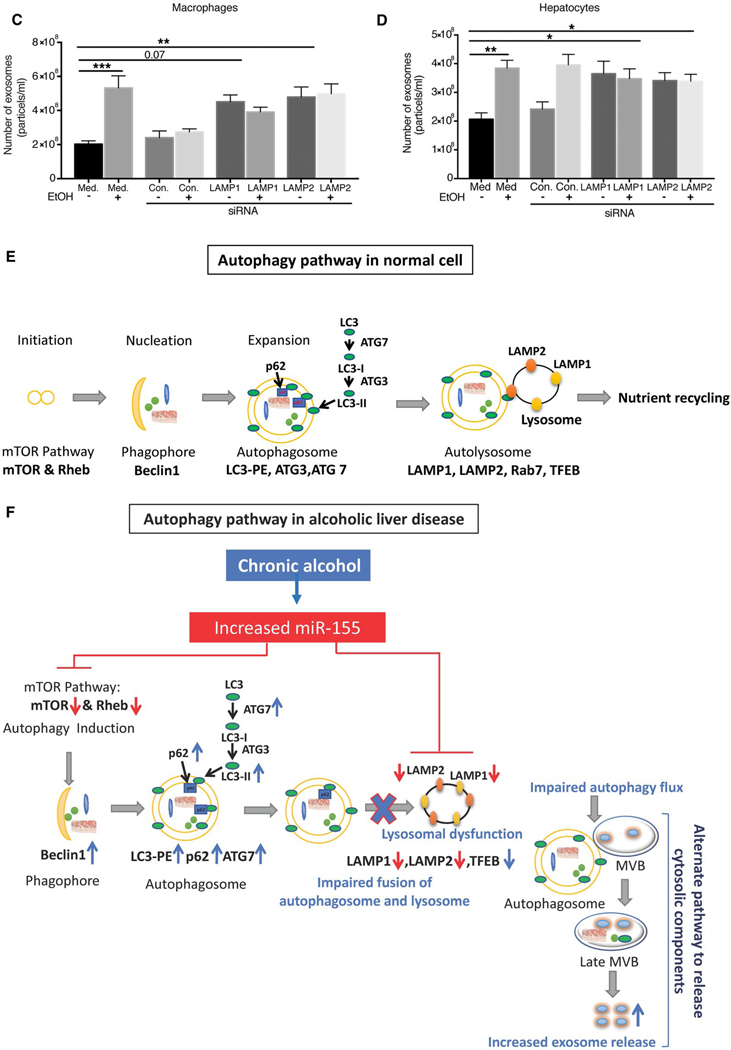
FIG. 8.
Knockdown of LAMP1 and LAMP2 increases exosome production in macrophages and hepatocytes. Macrophages (RAW 264.7) and hepatocytes (HEPA 1.6) were untreated or transfected with control or LAMP1 or LAMP2 siRNA, and the number of exosomes from supernatants of LAMP1/LAMP2 siRNA-treated macrophages and hepatocytes was quantified by NTA (A,B; n = 6). p62 (A,B) and LC3-I and LC3-II (A,B) were analyzed by western blotting using β-actin as a loading control (n = 6). The densitometry analysis is shown as bar diagrams. The number of exosomes from supernatants of LAMP1 and LAMP2 siRNA-treated macrophages and hepatocytes in the presence and absence of alcohol was quantified by NTA (n = 9; C,D). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. Schematic representation of miR-155-autophagy-exosome axis in ALD (E,F). Chronic alcohol induces miR-155, which then decreases mTOR and Rheb, thus inhibiting the mTOR pathway (E,F). Chronic alcohol increases Beclin1, Atg7, and LC3II expression. However, alcohol impairs autophagic flux by affecting LAMPs (LAMP1 and LAMP2) through miR-155. miR-155 regulates lysosome function by targeting LAMP1 and LAMP2. Because of impaired lysosome function, autophagosomes merge with MVBs to release their components outside the cell, and, as a consequence, there is increased exosomes secretion. Abbreviation: Med, medium.