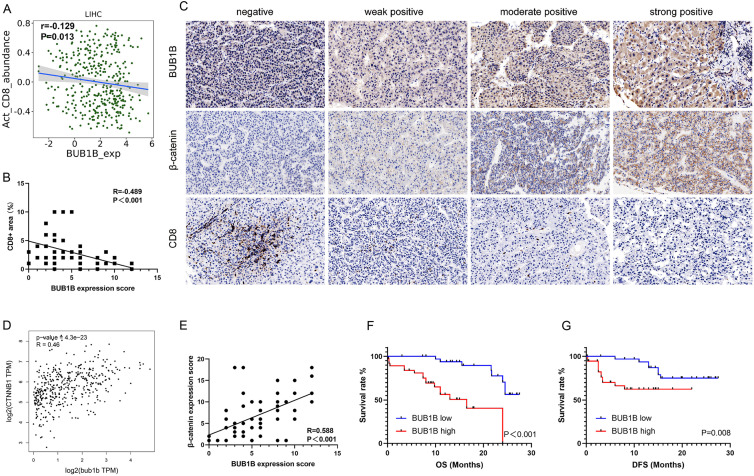
Figure 8.
BUB1B might be a potential target for immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). (A) Association of the BUB1B expression and CD8+ T-cell infiltration in HCC by TISIDB (r = −0.129, P = .013). (B) BUB1B expression level is negatively associated with CD8+ T-cell infiltration level validated in our 72 patients, tested by Spearman test (r = −0.489, P < .001). (C) Representative immunohistochemical staining of BUB1B, β-catenin, and CD8 in HCC. Negative, weak positive, moderate positive, and strong positive expression of BUB1B were shown, respectively. (D) Association of the BUB1B messenger RNA (mRNA) expression and β-catenin mRNA in HCC by GEPIA (r = 0.46, P < .001). (E) BUB1B expression level is positively associated with β-catenin expression level validated in our 72 patients, tested by Spearman test (r = −0.588, P < .001). (F) Overall survival (OS) curves of patients with HCC according to cancer expressed BUB1B levels (P < .001). (G) Disease-free survival (DFS) curves of patients with HCC according to cancer expressed BUB1B levels (P = .008).