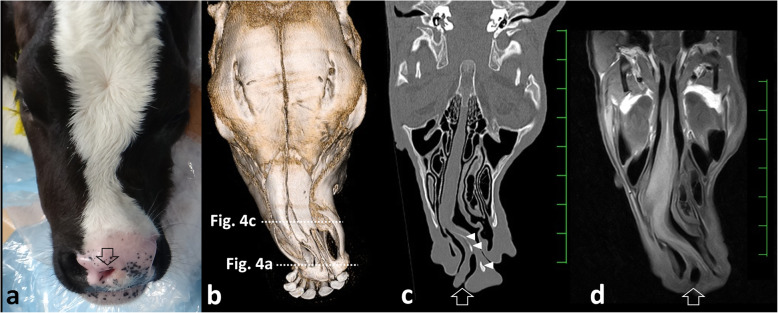
Fig. 2.
Dorsal macroscopic view of the nose (a), three-dimensional computed tomography (CT) visualizing the dorsal surface of the nasal bones (b), and dorsal CT (c) and T1-weighted MRI (d) visualizing the nasal cavity in the 1-month-old female Holstein calf. a The bridge of the nose is significantly curved toward the left. The middle nostril (empty arrow) is located in close proximity to the right nostril. b The transformation of the nasal bone allowed a curvature of approximately 30° from the central line of the nasal bone to the left. c The abnormal curve of the nasal septum allowed constriction within the right nasal cavity. The blind end is evident within the middle nostril (empty arrow). Bone-like structures (white arrowheads) are observed within the nasal septum. d A blind-ended middle nostril is evident (empty arrow), although a bone-like structure is not evident. Scale: 25 mm on CT and MRI