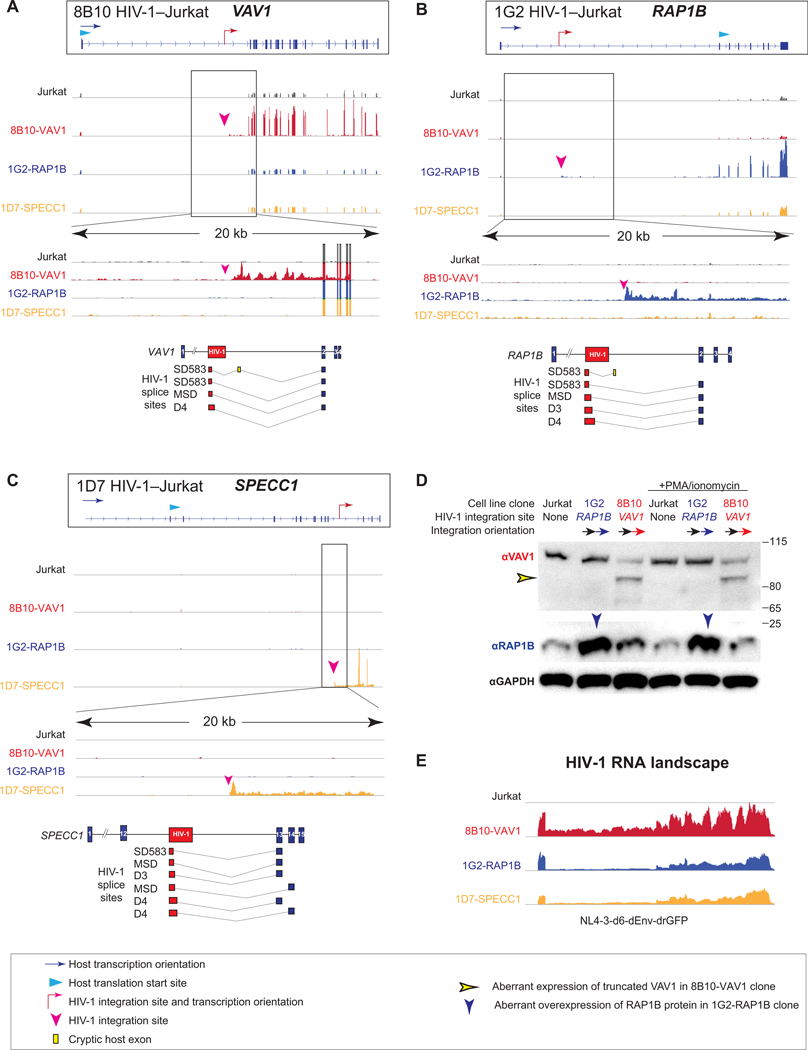
Fig. 6. HIV-1 drives aberrant cancer-related gene transcription and induces aberrant protein expression at the integration site.
(A to C) HIV-1 integration effect on the transcription of cancer-related genes VAV1 in HIV-1–Jurkat clone 8B10 (A), RAP1B in HIV-1–Jurkat clone 1G2 (B), and SPECC1 in HIV-1–Jurkat clone 1D7 (C) at the integration sites. Normalized RNA transcription landscapes with enlarged 20-kb windows across integration sites. HIV-1 proviruses are integrated downstream of the translation start site of VAV1 and SPECC1 in HIV-1–Jurkat clones 8B10 and 1D7, respectively. HIV-1 integration is upstream of the translation start site of RAP1B in HIV-1–Jurkat clone 1G2. HIV-1–host chimeric RNA captured in RNA-seq is depicted as HIV-1 RNA (red boxes), splice junction (gray lines), canonically spliced host exons (blue boxes), and cryptic host exons (yellow bars). (D) Western blot of VAV1 and RAP1B expression in HIV-1–Jurkat clones. The blue arrowhead indicates HIV-1–driven RAP1B protein expression, and the yellow arrowhead indicates HIV-1–driven truncated VAV1 protein expression. αGAPDH, anti–glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (E) HIV-1 genomic RNA landscape in HIV-1–Jurkat T cell clones.