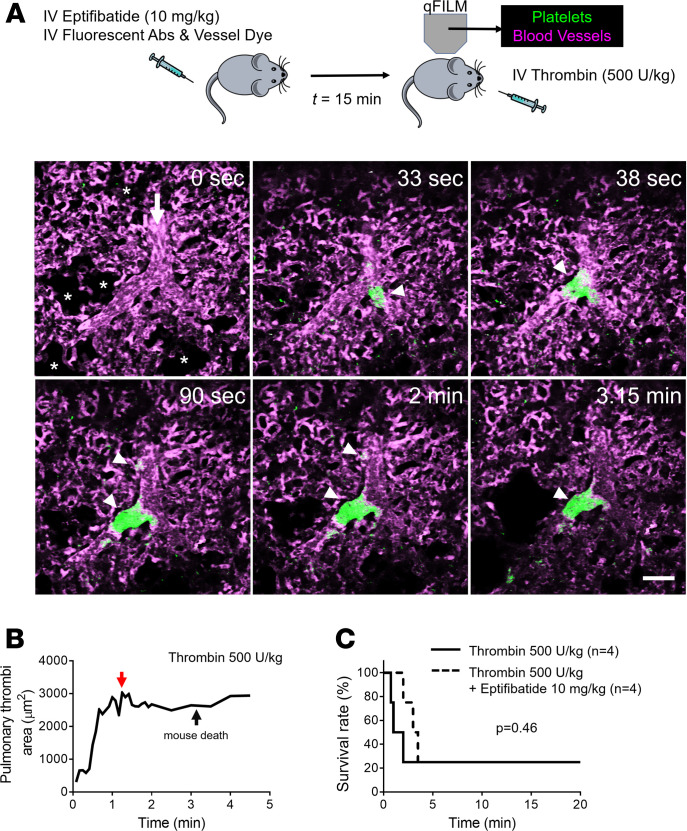
Figure 4. Thrombin-triggered lethal pulmonary thrombosis is platelet-αIIbβ3 independent.
(A) WT mice were intravascularly (IV) administered 500 U/kg thrombin with or without IV administration of 10 mg/kg αIIbβ3 inhibitor (eptifibatide) 15 minutes before IV thrombin. Pulmonary circulation was imaged using quantitative fluorescence intravital lung microscopy (qFILM). qFILM images of the same field of view (FOV) at 6 different time points are shown to assess the effect of 10 mg/kg IV eptifibatide on the development of 500 U/kg IV thrombin-dependent pulmonary thrombosis. t = 0 seconds (s) corresponds to time point before and t > 0 s correspond to time points immediately following IV thrombin administration. Pulmonary thrombosis was absent at t = 0 s. Following 500 U/kg IV thrombin, medium (500–1000 μm2) and large (>1000 μm2) platelet-rich thrombi (white arrowheads) sequestered in the pulmonary arteriole and traveled down the pulmonary arterioles to occlude the arteriolar bottlenecks (t = 90 s). The mouse died at t = 3.15 minutes, leading to arrest of pulmonary blood flow, which was evident by the presence of stationary erythrocytes (Supplemental Video 7) and decrease in vascular dye (purple fluorescence) in the FOV. Platelets (green) and pulmonary microcirculation (purple). Asterisks denote the alveoli. White arrow mark the direction of blood flow. The diameter of the arteriole is 33 μm. Scale bar: 50 μm. See also Supplemental Video 7 for the complete qFILM time series. (B) Pulmonary thrombi area plotted as a function of time for the FOV shown in A. Red and black arrows indicate pulmonary thrombi maximum area and the time of mouse death, respectively. (C) Survival rate during qFILM experiments in WT mice pretreated (n = 4 mice) or untreated (n = 4 mice) with 10 mg/kg IV eptifibatide before 500 U/kg IV thrombin (P = 0.46, log-rank test).