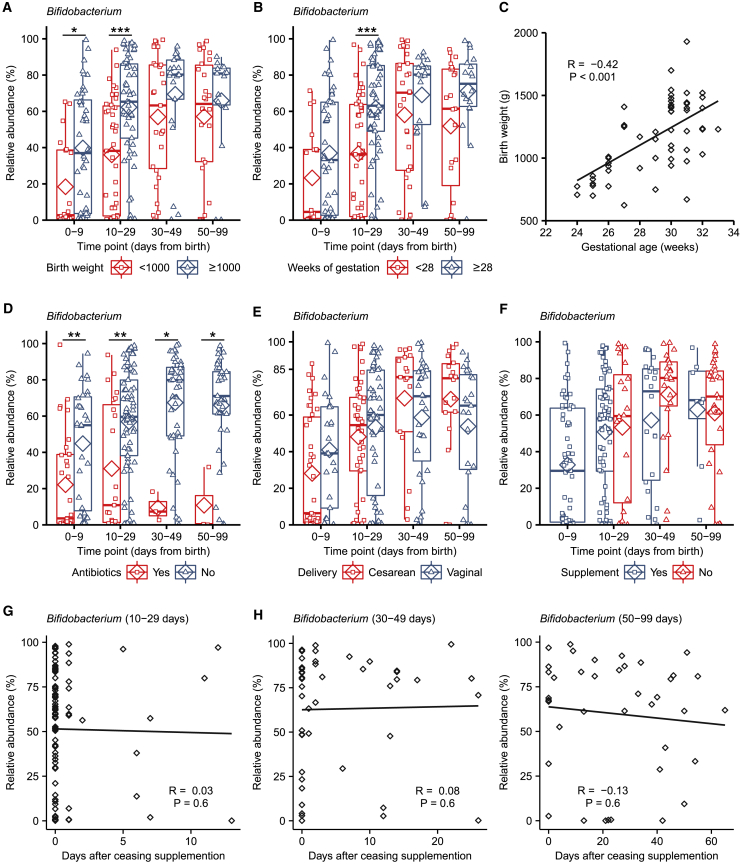
Figure 3.
Effects of Birth Weight, Antibiotic Use, Delivery Mode, and Bifidobacterium Colonization in Bif/Lacto Group Infants
(A) Bifidobacterium abundance between very low birth weight (<1,000 g) and low birth weight (>1,000 g) in Bif/Lacto infants (N = 0–9: <1,000 = 20, ≥1,000 = 44; 10–29: <1,000 = 43, ≥1,000 = 57; 30–49: <1,000 = 27, ≥1,000 = 21; 50–99: <1,000 = 26, ≥1,000 = 15).
(B) Bifidobacterium abundance between very low gestational age (<28 weeks) and low gestational age (≥28 weeks) Bif/Lacto infants (N = 0–9: <1,000 = 18, ≥1,000 = 46; 10–29: <1,000 = 43, ≥1,000 = 57; 30–49: <1,000 = 29, ≥1,000 = 19; 50–99: <1,000 = 23, ≥1,000 = 18).
(C) Infant birth weight in grams correlated with gestational age in weeks (n = 100).
(D) Bifidobacterium abundance in Bif/Lacto infants receiving antibiotics at the time of sample collection (N = 0–9: Yes = 33, No = 31; 10–29: Yes = 23, No = 77; 30–49: Yes = 3, No = 44; 50–99: Yes = 3, No = 37).
(E) Bifidobacterium abundance in Bif/Lacto infants delivered by caesarean or vaginal birth (N = 0–9: C = 39, V = 25; 10–29: C = 46, V = 54; 30–49: C = 17, V = 31; 50–99: C = 18, V = 23).
(F) Bifidobacterium abundance in Bif/Lacto infants still receiving or no longer receiving supplementation (N = 0–9: Yes = 63; 10–29: Yes = 77, No = 20; 30–49: Yes = 22, No = 23; 50–99: Yes = 8, No = 30).
(G) Bifidobacterium abundance in Bif/Lacto infants by days after ceasing supplementation at 10–29 days of age (n = 97).
(H) Bifidobacterium abundance in Bif/Lacto infants by days after ceasing supplementation at 30–49 days of age (n = 45).
(I) Bifidobacterium abundance in Bif/Lacto infants by days after ceasing supplementation at 50–99 days of age (n = 38).
Boxplots show group median and interquartile range, diamonds indicate the group mean, and individual points highlight individual infant samples. Asterisks represent p values: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figure S3 and Data S7.