Figure.
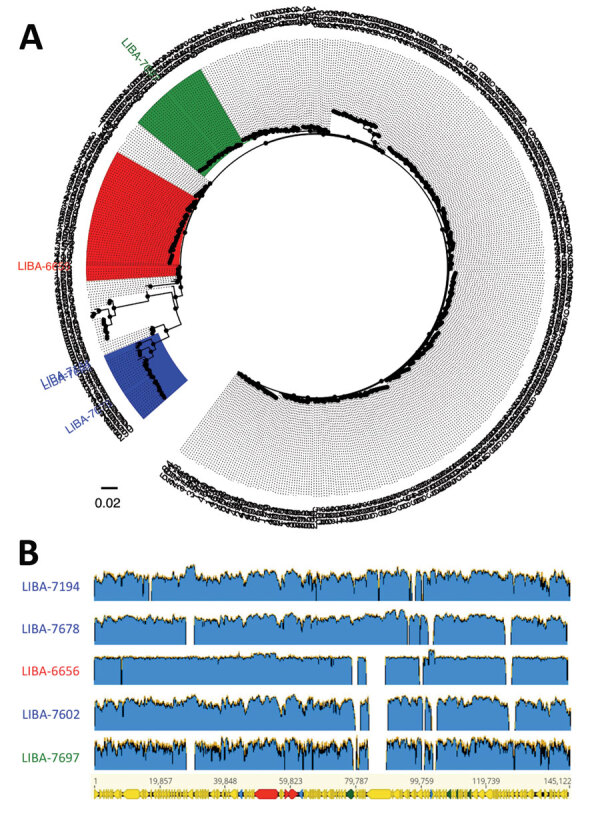
Multilocus sequence typing–based classification (A) and diversity of extrachromosomal circular sequences (B) of Clostridioides difficile strains with plasmid-encoded toxins. A) FastTree (http://www.microbesonline.org/fasttree) phylogenic tree derived from a MUSCLE (http://www.drive5.com/muscle) alignment of concatenated multilocus sequence typing alleles from all C. difficile sequence types deposited in the PubMLST database (https://pubmlst.org). Tip labels represent sequence types or strain names. Strains from clade C-I are highlighted in blue, from clade 2 in red, and from clade 4 in green. B) This graphic shows short reads from strains LIBA-7194, LIBA-7678, LIBA-7602 (clade C-I, blue), LIBA-6656 (clade 2, red), and LIBA-7697 (clade 4, green) mapped to the plasmid sequence of strain HSJD-312, which was obtained through hybrid PacBio (Pacific Biosciences, https://www.pacb.com) and Illumina (Illumina, https://www.illumina.com) sequencing and therefore used as a reference (145.1 kb, bottom). Arrows in the reference sequence represent annotated coding sequences. Genes for toxins are in red; for transposases, integrases, and recombinases are in blue, and for proteins from a putative conjugation machinery are in green.
