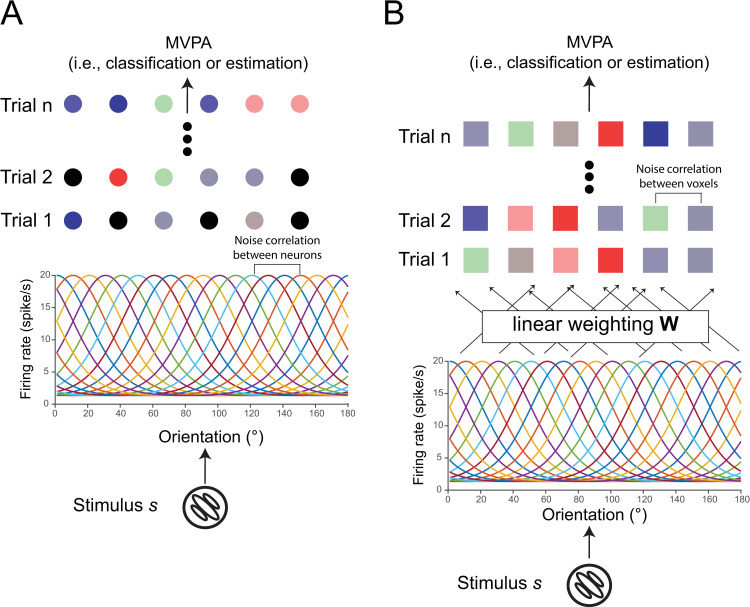
Fig 2. Neuron- and voxel-encoding models.
The neuron-encoding model (panel A) proposes a neuronal population with orientation-selective tuning curves. Each neuron has Poisson-like response variance and the noise correlation between two neurons can be specified with different structures and strength (see Materials and Methods). The voxel-encoding model proposes a similar neuronal population and the response of a single voxel is the linear combination of the responses of multiple neurons. The noise correlation between two voxels can be specified using similar methods (see Materials and Methods). Note that voxelwise NCs can come from the response variability at both neuronal and voxel levels (see Fig 6). Using the neuron- and the voxel-encoding models, we can generate many trials of neuronal and voxel population responses and perform conventional MVPA on the simulated data. The goal is to examine multivariate decoding performance as a function of the NC structure and strength between either neurons or voxels.