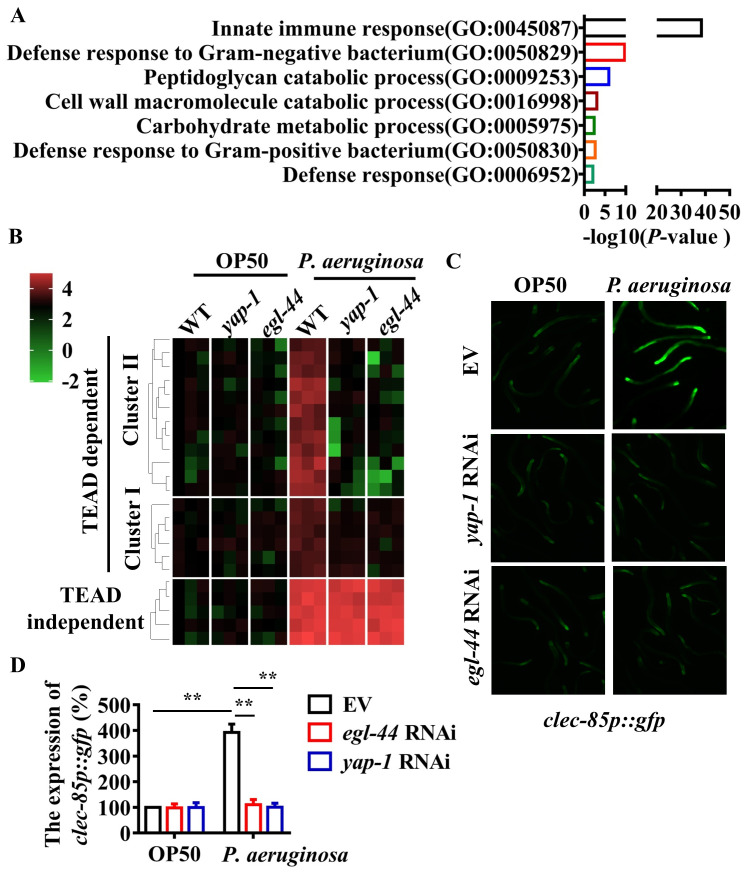
Fig 2. EGL-44/TEAD and YAP-1/YAP regulate the expression of immune-related genes after P. aeruginosa infection.
(A) Enrichment analysis of the GO biological process of the P. aeruginosa-regulated genes containing CATTCC DNA motifs is shown. The enrichment P value of each term was transformed to a -log10(P-value). (B) Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of expression levels (qRT-PCR) of YAP-1-EGL-44 complex-dependent immune-related genes as well as YAP-1-EGL-44 complex-independent genes in worms exposed to P. aeruginosa (24 h) by using Origin 2019b. Each column represents an independent replicate. (C) Expression of clec-85p::gfp was upregulated in worms infected with P. aeruginosa compared to worms fed E. coli OP50. Knockdown of egl-44 and yap-1 by RNAi reduced such an increase of clec-85p::gfp expression. (D) Quantification of GFP levels. These results are means ± SD of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01 relative to OP50 (n ≥ 50 worms per experiment) (One-way ANOVA followed by a Student-Newman-Keuls test).