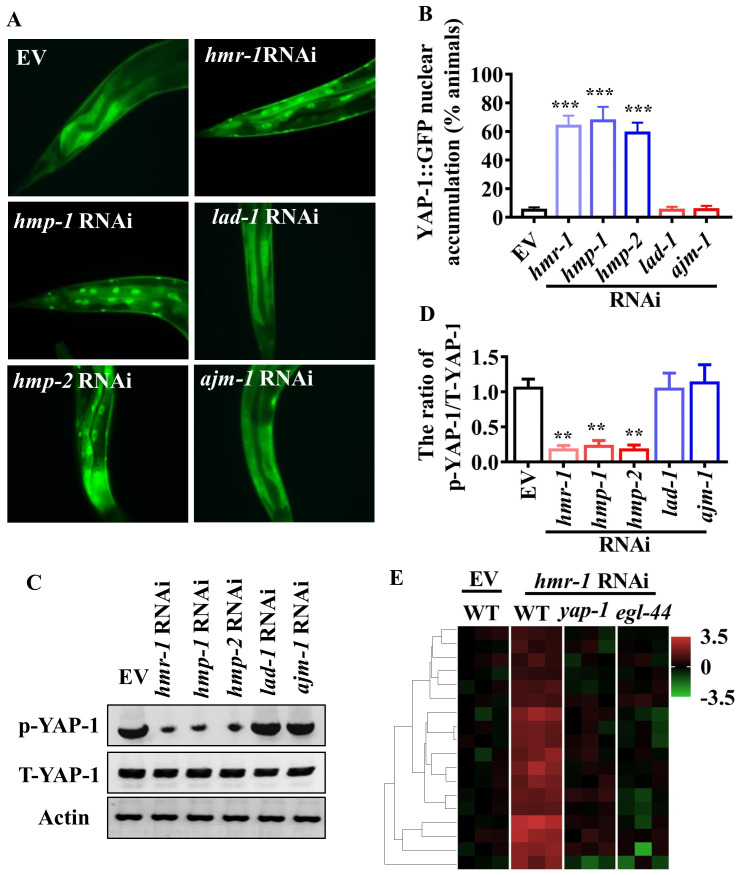
Fig 5. Disruption of adherens junction components leads to activation of YAP-1/YAP.
(A) Knockdown of hmr-1, hmp-1, and hmp-2, but not lad-1 and ajm-1 by RNAi induced nuclear translocation of YAP-1::GFP in worms fed nonpathogenic E. coli OP50. (B) Quantification of YAP-1 nuclear accumulation (n = 3 independent experiments, n = 100/condition). ***P < 0.001 relative to empty vector (EV) (Two-sample t-test). (C) The levels of phosphorylated YAP-1 (p-YAP-1). The blot is typical of three independent experiments. (D) Quantification of the ratio of p-YAP-1 to total YAP-1 (T-YAP-1). These results are means ± SD of three experiments. **P < 0.01 relative to EV (Two-sample t-test). (E) Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of expression levels (qRT-PCR) of immune-related genes in hmr-1 RNAi-treated worms fed E. coli OP50 (24 h) by using Origin 2019b. Each column represents an independent replicate. Mutations in yap-1(tm1416) and egl-44(mt2247) reduced the expression of these genes in the worms.