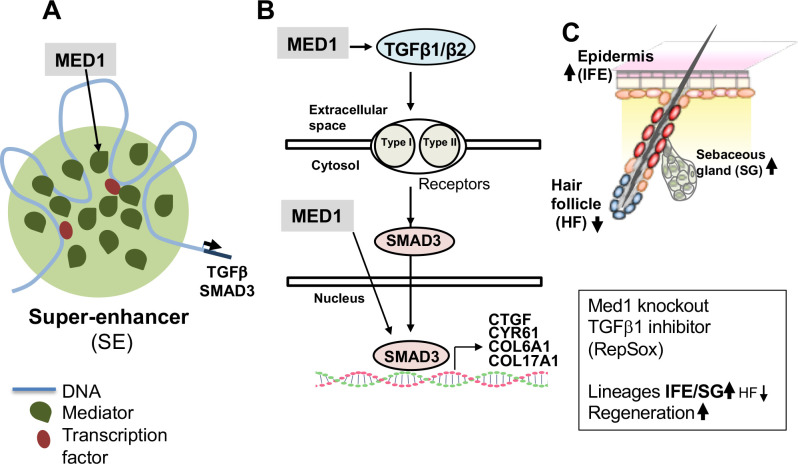
Fig 6. A proposed model in which Med1 regulates TGFβ signaling, epidermal lineages and regeneration.
(A) Med1 mediates transcription of TGFβ1/β2 and SMAD3. Mediator (green) including Med1 subunit is densely incorporated into large super-enhancers (SE) that drive selected genes involved with lineage maintenance and tissue regeneration [9]. (B) Med1 induces TGFβ1/β2 and SMAD3 (arrows) to support TGFβ downstream target gene expression (e.g. CTGF, COL6A1) that may maintain cell quiescence or epidermal lineages. (C) Med1 null skin increases epidermal lineages but suppresses HF lineage. Med1 and TGFβ signaling may have distinct but overlapping roles in regulating different lineages as described in results and discussion. TGFβ inhibition by RepSox (5d) recapitulates the phenotypes of Med1 null skin with respect to accelerated wound re-epithelialization, providing a potential new approach to treating diseases such as delayed wound healing.