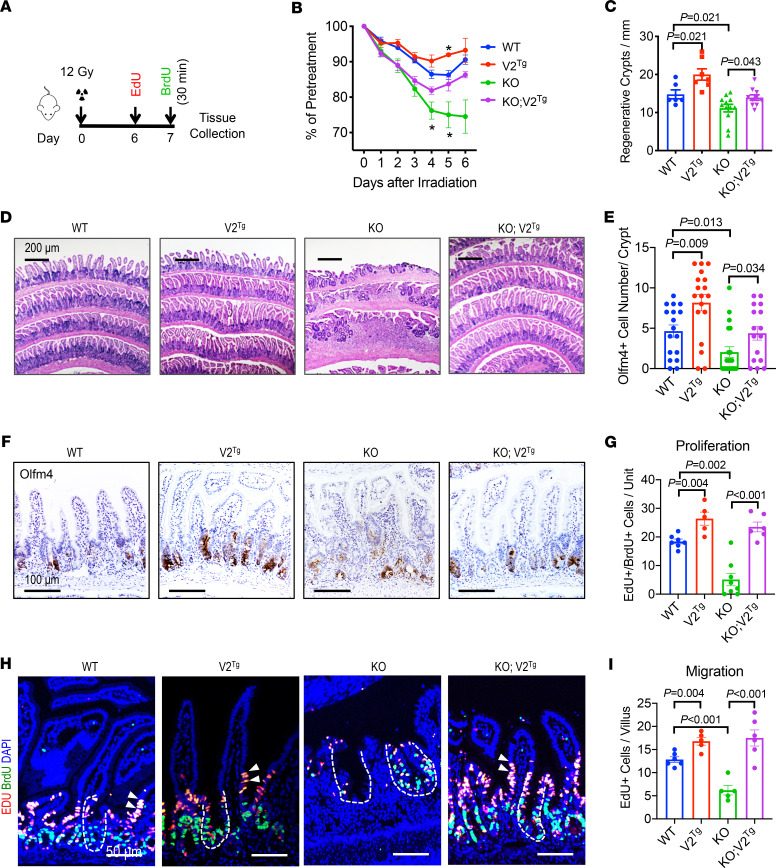
Figure 6. Elevating the epithelial Cdc42-MAPK program mitigates mucosal damage following ISC loss.
(A) Mice received a 12 Gy total-body irradiation and were sacrificed 7 days after irradiation. Cycling IECs were labeled by sequential injection of EdU (1 day) and BrdU (30 minutes) before sacrifice. (B) Percentage of body weight changes were presented as averages of each genotype group (N = 8 per genotype). Note there was death of KO animals during the experiment following irradiation. Asterisks indicate P < 0.05 compared with WT mice. (C) Average numbers of regenerative crypts per millimeter were counted from multiple ileal sections of 3 postirradiation animals per genotype. (D) H&E-stained postirradiation mouse ileal sections of various genotypes 3 days after irradiation. (E and F) Olfm4+ cells were counted from immunohistochemistry performed on multiple ileal sections of 3 postirradiation animals per genotype. Representative images show Olfm4 staining of different genotypes 3 days after irradiation. (G and H) EdU (red) and BrdU (green) were stained. Average numbers of EdU- and BrdU-labeled IECs per crypt-villus unit were quantified from multiple sections of 3 postirradiation animals per genotype. Dashed lines indicate crypts; white arrows point to EdU+ and BrdU+ IECs migrating to villi. Nucleus was counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 50 μm. (I) Average numbers of only EdU-labeled IECs in upper crypt and villus region were quantified from multiple sections of 3 postirradiation animals per genotype. Please also see Supplemental Figure 6.