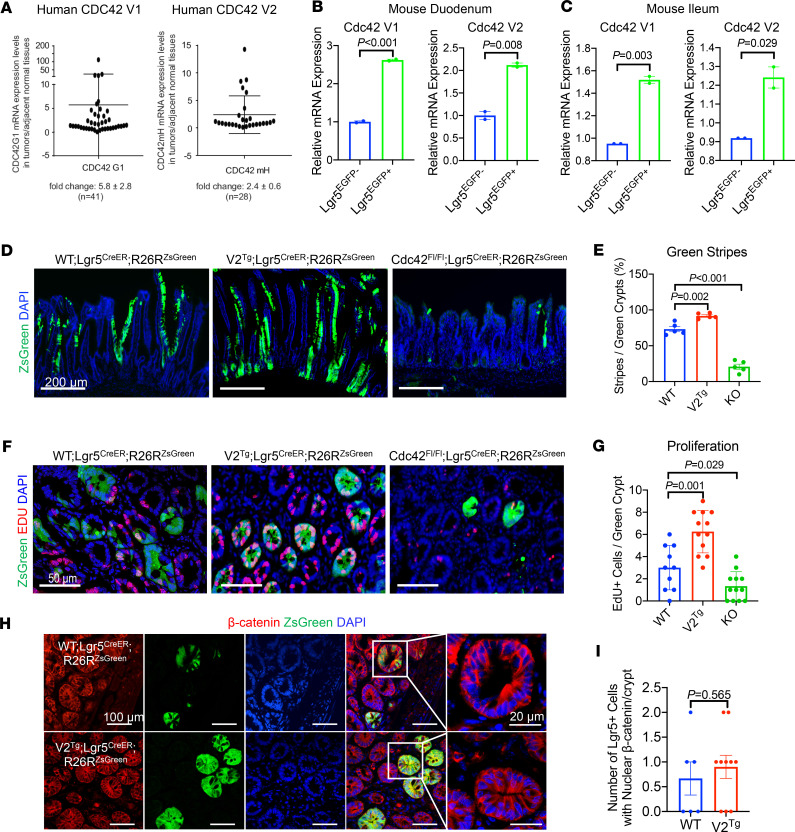
Figure 7. Elevating Cdc42 in ISCs promotes injury-induced regeneration.
(A) TaqMan RT-PCR for human CDC42-V1 and -V2 mRNA was performed on colon tumor tissues and adjacent nontumor tissues. Data were graphed as ratio of tumor over adjacent tissue. Elevated CDC42-V1 was shown in 27 out of 41 tumors while 12 out of 28 tumors had elevated CDC42-V2. (B) Quantitative PCR for mouse Cdc42 variants was performed on FACS-sorted Lgr5EGFP+ versus Lgr5EGFP– IECs from WT mouse duodenums. (C) Quantitative PCR for mouse Cdc42 variants was performed on FACS-sorted Lgr5EGFP+ versus Lgr5EGFP– IECs from WT mouse ileums. (D and E) Lineage tracing of Lgr5 ISCs of distinct (Cdc42-WT, V2Tg, or KO) genotypes 7 days after irradiation using an R26RZsGreen reporter. EdU was injected 6 hours before sacrifice to identify cycling ISC descendants. Lineage tracing events were presented as percentage of observed green stripes out of total number of green crypts within the same field. Data represent multiple sections from 2 postirradiation animals. Note that V2Tg and KO ISCs showed increased and diminished lineage tracing events. (F and G) The average numbers of EdU+ cells per green crypt were quantified from multiple sections of 2 postirradiation animals. (H and I) The average numbers of nuclear β-catenin+ cells per green crypt were quantified from multiple sections of 2 postirradiated Lgr5CreER-IRES-EGFP R26RzsGreen Cdc42-WT and Lgr5CreER-IRES-EGFP R26RzsGreen V2Tg mice.