Fig. 2. Nanoparticle encapsulation enhances the uptake and immunostimulatory potency of DMXAA.
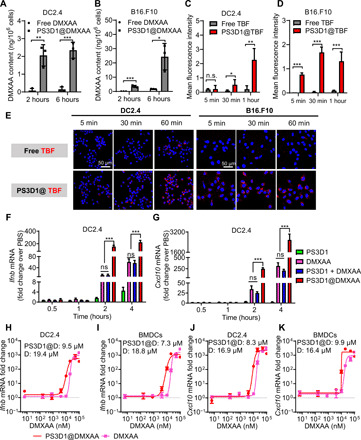
(A and B) High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis of intracellular DMXAA concentrations in DC2.4 and B16.F10 cells after treatment with different formulations for 2 and 6 hours. (C to E) Confocal laser scanning microscopy images (E) of DC2.4 and B16.F10 cells upon incubation with free TBF and PS3D1@TBF for varying time intervals (scale bars, 50 μm), and mean fluorescence intensity analysis of TBF uptake in DC2.4 (C) and B16.F10 cells (D). (F and G) qPCR analysis of Ifnb (F) and Cxcl10 (G) gene expression in DC2.4 after treatment with different formulations for varying time intervals. n = 3 biologically independent samples. (H and I) Dose-response curves of the Ifnb response elicited by indicated PS3D1@DMXAA nanoparticles and DMXAA in DC2.4 (H) and BMDCs (I). (J and K) Dose-response curves of the Cxcl10 response elicited by indicated PS3D1@DMXAA nanoparticles and DMXAA in DC2.4 (J) and BMDCs (K). n = 3 biologically independent samples. PS3D1@D, PS3D1@DMXAA; D, DMXAA. Data are means ± SD, and statistical significance was calculated by two-tailed Student’s t test: ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, and *P < 0.05; ns, not significant.
