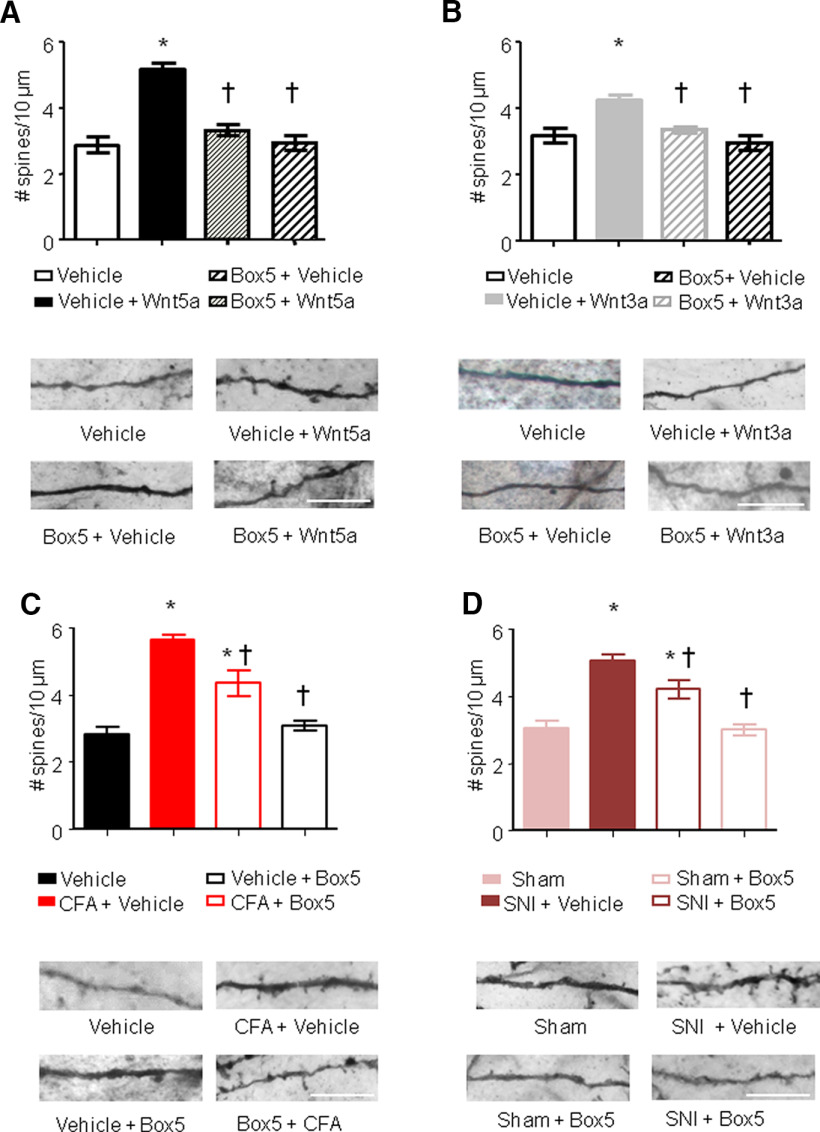
Figure 3.
Spinal Wnt5a induces remodeling of synaptic spines in spinal dorsal horn neurons. A–D, Quantification of synaptic spine density in spinal neurons (primarily of lamina V origin) in vivo following intrathecal injection of Wnt5a (2 µg/5 µl; A), intraplantar injection of Wnt3a (10 ng/20 µl; B), 24 h after CFA injection (C) or 7 d after nerve lesion (D), in the presence or absence of intrathecal administration of Box5, a Wnt5a signaling inhibitor. Examples of high-magnification views of microscopic images of labeled dendrites with synaptic spines are shown below the corresponding bar graphs. Scale bar, 10 μm; N = 3–4 animals/condition, 20–30 neurons, 500–700 spines counted were analyzed. Two-way ANOVA for random measurements, followed by Bonferroni's test, was performed. *p < 0.05 compared with control group (vehicle or sham treated); †p < 0.05 compared with the group that received only the nociceptive stimuli but not the inhibitor. In all panels, data are represented as the mean ± SEM.