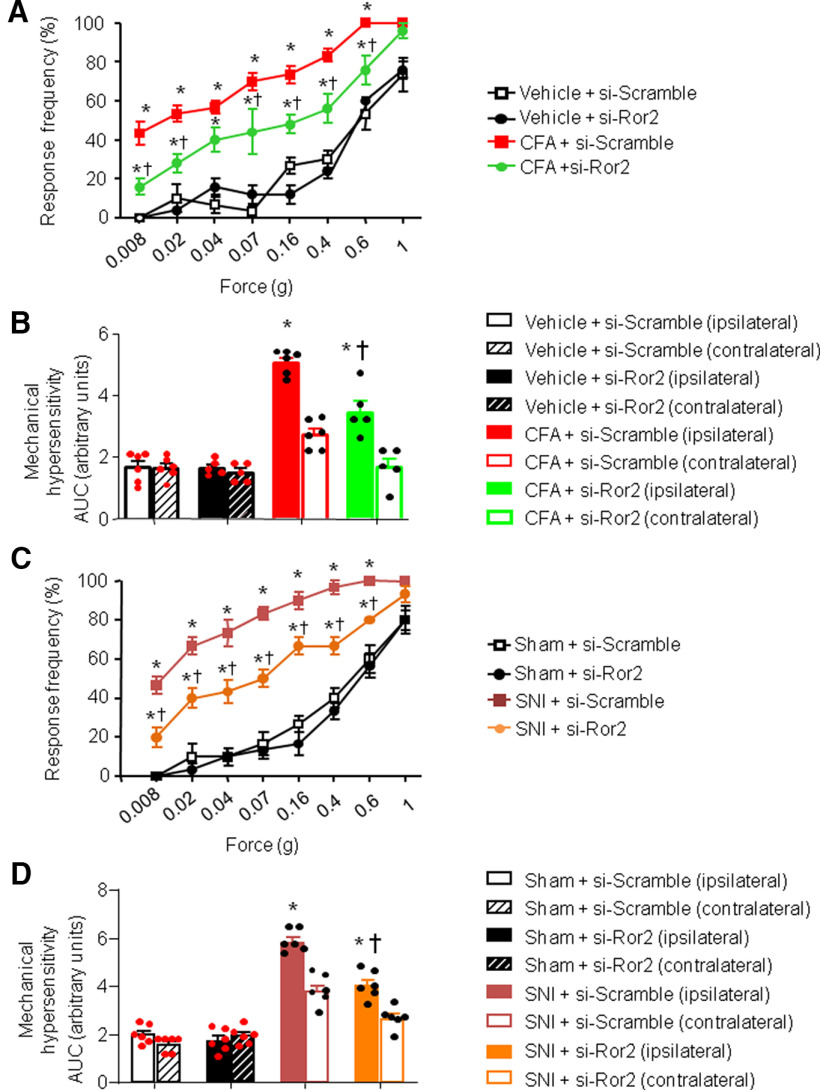
Figure 6.
Spinal Ror2 contribute to nociceptive hypersensitivity in mouse models of chronic pain. A–D, Behavioral analysis of the effects of intrathecal administration of siRNA against Ror2 on mechanical sensitivity 24 h after intraplantar injection of CFA-induced unilateral paw inflammation (A, B) or 7 d after unilateral nerve injury (SNI; C, D). Stimulus–response curves of the ipsilateral paw are shown in A and C, whereas the integral over time (AUC) for the inflamed or injured paw (ipsilateral) as well as the contralateral paw are shown in B and D. In all panels, N = 8 mice/group; ANOVA for repeated measures was performed, followed by Tukey's test; *p < 0.05 compared with the corresponding control group; †p < 0.05 compared with CFA-treated (A, B) or SNI-treated (C, D) animals. In all panels, data are represented as the mean ± SEM, and bar graphs are also shown as scatter plots.