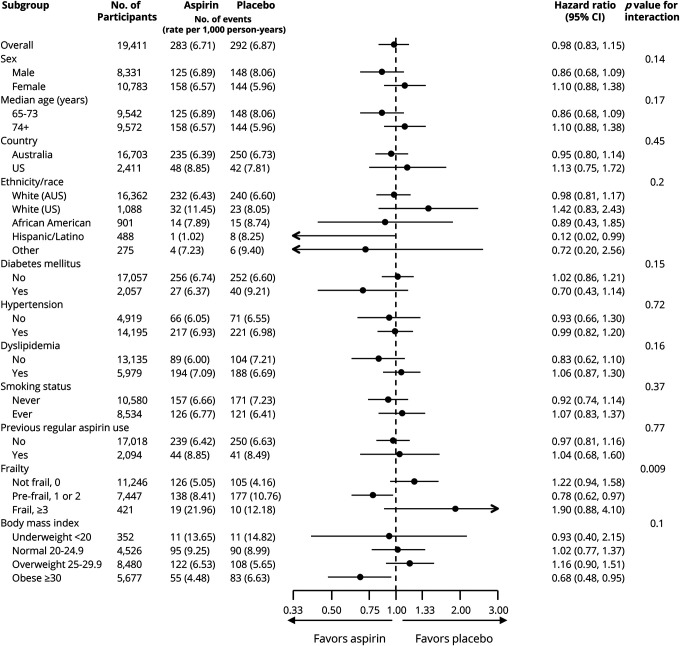
Figure 3. Forest plot for adjudicated incidence of dementia (all-cause) in prespecified subgroups.
Arrows indicate that the 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were beyond the scale. Other ethnic/racial group included individuals who were not Hispanic but who did not state another race or ethnic group (18), or any other category with fewer than 200 participants overall. This included Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander (12 participants), Native American (6), multiple races or ethnic groups (64), and Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander (11). The presence of diabetes was based on participants’ report of diabetes mellitus or a fasting glucose level of at least 126 mg/dL (≥7 mmol/L) or receipt of treatment for diabetes. Hypertension was defined as treatment for high blood pressure or a blood pressure of greater than 140/90 mm Hg at trial entry. Dyslipidemia was defined as the receipt of cholesterol-lowering medication or as a serum cholesterol level of at least 212 mg/dL (≥5.5 mmol/L) in Australia and at least 240 mg/dL (≥6.2 mmol/L) in the United States or as a low-density lipoprotein level of more than 160 mg/dL (>4.1 mmol/L). Previous regular aspirin use was defined according to participant-reported regular use of aspirin immediately before the first baseline visit, with a 1-month washout period before randomization. Frailty was categorized on the basis of the adapted Fried frailty criteria, which included body weight, strength, exhaustion, walking speed, and physical activity. The category of prefrail included participants who met 1 or 2 criteria, and the category of frail included those who met 3 or more criteria. Body mass index is the weight in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters.