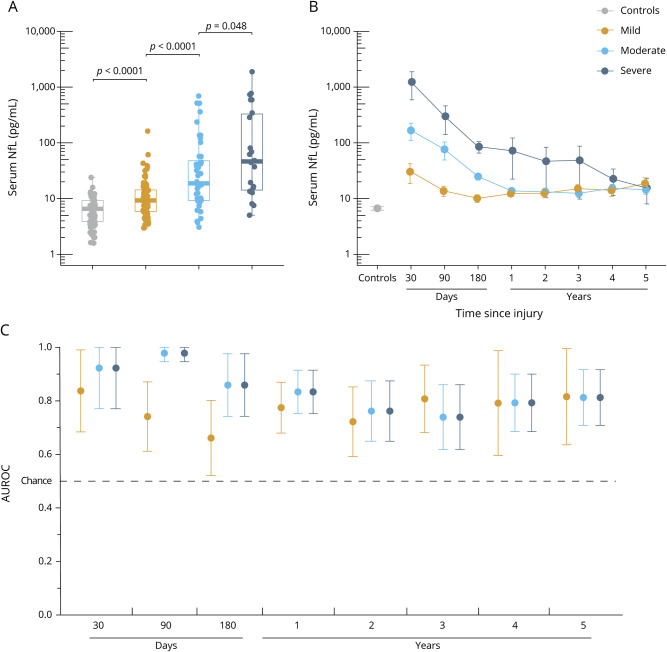
Figure 3. Serum NfL shows diagnostic utility in patients with subacute and chronic TBI.
(A) Serum concentrations of neurofilament light (NfL) measured at enrollment (median 7 months after injury) across traumatic brain injury (TBI) severity and controls. The p values are from the Kruskal-Wallis test, adjusted for multiple comparisons with the Benjamin-Hochberg procedure. (B) Serum NfL over time in patients with longitudinal data. The y-axes of plots A and B are log-transformed for visual clarity. (C) Diagnostic accuracy (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve [AUROC], error bars indicate 95% confidence interval) of serum NfL measured at different time points after injury vs controls. Boxplots show the median and interquartile range.