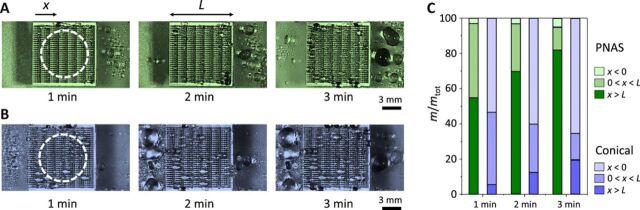
Fig. 4. Large-scale droplet rectification.
(A) Top view of centimetric samples subject to fog (released 3 cm above the central part, as marked with dashes), as a function of time. PNAS not only rectifies the flux of water droplets but also ejects it out of the rectifying unit. (B) Same experiment on inclined conical fibers. Rectification is less efficient and takes place in the opposite direction. Photo credit: Shile Feng, City University of Hong Kong. (C) Water repartition e = m/mtot defined as the proportion of the injected water found on the different sections of the sample, that is, x < 0, 0 < x < L, and x > L. Repartition is compared on PNAS (green columns) and inclined cones (blue columns) at different times.