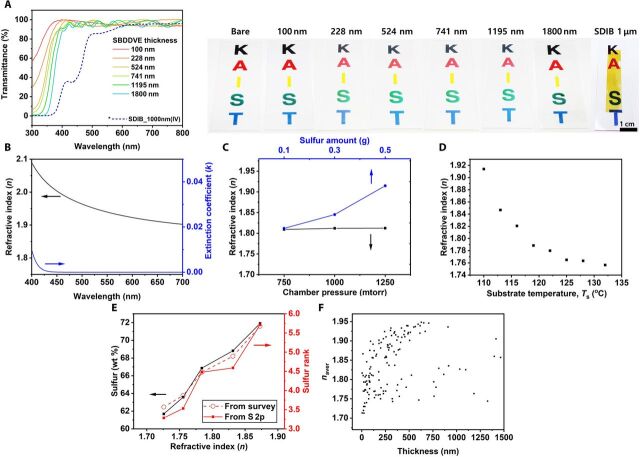
Fig. 4. Optical properties of the sCVD films.
(A) Transmittance spectra of SBDDVE from sCVD with thickness ranging from 100 nm to 1.8 μm and SDIB from inverse vulcanization with a thickness of 1.0 μm with digital photographs of corresponding films coated on glass slides. (B) Refractive index (n) and extinction coefficient (k) of 500-nm-thick SBDDVE obtained using spectroscopic ellipsometry. (C) The sulfur loading amount (blue; with the fixed process pressure of 1000 mtorr and Ts = 110°C), the chamber pressure (black; with the fixed sulfur amount of 0.1 g and Ts = 110°C), and (D) the substrate temperature (with the fixed sulfur loading amount of 0.5 g and the process pressure of 1000 mtorr). (E) The sulfur weight ratio in SBDDVE calculated from XPS survey scan (black), sulfur rank calculated from XPS survey scan (red dash), and sulfur rank calculated from XPS S 2p high-resolution scan (red solid) with respect to the corresponding refractive index. (F) The average refractive index from 400 to 700 nm versus thickness plot of SBDDVE synthesized by sCVD. Photo credit: Wontae Jang (Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology) and Jisung Choi (Kyung Hee University).