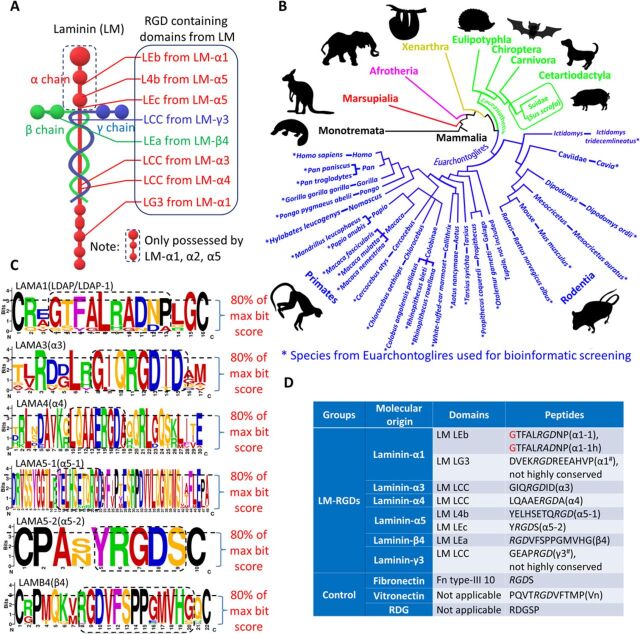
Fig. 1. Evolutionary conservation and motif analysis enable identification of LM-derived RGD peptides for microarray construction.
(A) LM structural diagram with location of all RGD-containing domains. (B) Schematic diagram showing the species of Euarchontoglires used for bioinformatic alignment screening (*) in context of their phylogenetic relationship. Different colors indicate each subfamily from Mammalia. (C) Bitmap plots of motif analysis of the highly conserved sequences among species in Euarchontoglires. Dashed-line boxes from bitmap plots determine the highly conserved positions around/at RGD (80% of max bit score set as the filter criteria). The most repeated amino acid (signified by size of letter) from each conserved peptide position was used as the representative amino acid for synthesis. (D) The list of identified consensus LM-RGD sequences from motif analysis and their correspondent origin domains (Fn-RGD and Vn-RGD included as the positive controls) for LM-RGD microarray screening. Glycine in red as the linker for the peptides from LM-α1 was optimized by following experiments.