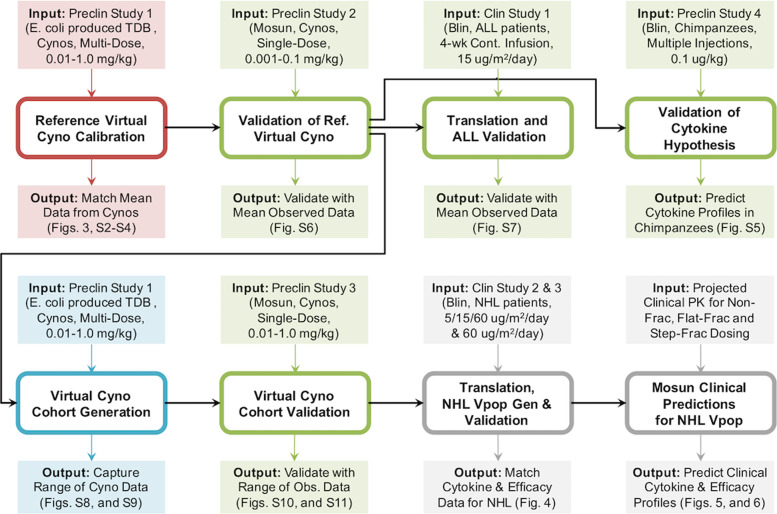
Fig. 2. Workflow of mosunetuzumab QSP model development.
The QSP model was calibrated using multiple dose preclinical data of E. coli produced anti-CD20/CD3 TDB in cynomolgus monkeys (preclinical study 1, 0.01–1 mg/kg). The outcome was a reference virtual cyno, which reproduces the dynamics of cytokines, B and T-cells in the PB and lymphoid tissues. The model was then validated against data from the single-dose mosunetuzumab in cynomolgus monkeys (preclinical study 2, 0.001–0.1 mg/kg) by using the reference virtual cyno to predict the B and T-cell profiles. Next, the reference virtual cyno was translated to the human ALL patient using the appropriate physiological volume and T and B-cell numbers for different tissues and including blinatumomab PK and its downstream effects on T-cell activation and B-cell killing. The model was successfully validated against the clinical data from blinatumomab in ALL patients. In addition, we used reference virtual cyno and human models to validate the cytokine hypothesis by predicting the IL6 Levels measured in chimpanzees treated with multiple weekly injections of blinatumomab (preclinical study 4). To capture the observed variability in cyno measurements, we generated a virtual cohort of healthy cynos using the range of observed measurements in the multiple dose study of mosunetuzumab in cynomolgus monkeys (preclinical study 1) and validated against the single-dose mosunetuzumab in cynomolgus monkeys (Preclinical study 3, 0.01–1.0 mg/kg). We generated a virtual NHL population by translating the virtual cohort of healthy cynos, adding a tumor compartment by implementing a large B-cell dense mass using human physiology and including additional disease-related variability such as baseline peripheral B and T-cells, tumor load, tumor cell doubling time and revised B:T ratio in the tumor microenvironment. The virtual NHL population matched the distribution of antitumor efficacy and cytokine time profiles following blinatumomab treatment. This population was subsequently used to predict and compare the time course of systemic cytokine levels and antitumor efficacy for different dosing regimens of mosunetuzumab.