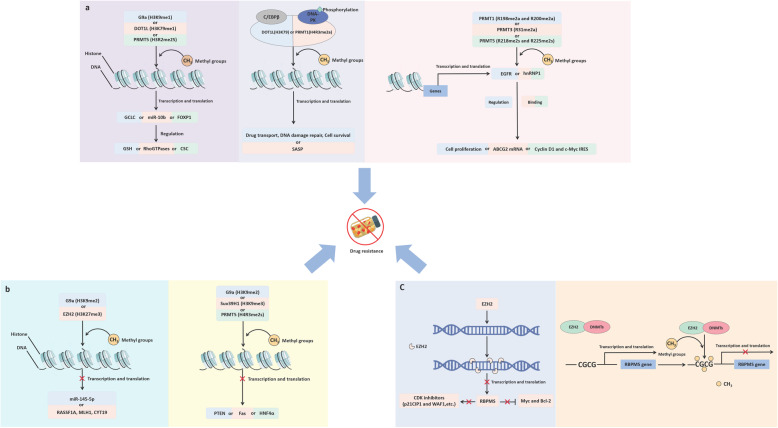
Fig. 3.
The mechanism of HMT induced drug resistance. a, KMTs and PRMTs catalyze the methylation of gene promoters (3a left) or transcription start sites (3b middle) alone or with other molecules (3b right), which activates the transcription of downstream drug resistance-related genes, resulting in drug resistance. PRMTs promote the binding of proteins to other molecules by catalyzing protein arginine residue, leading to drug resistance. b, KMTs and PRMTs catalyze methylation of promoter (3b right) or “unknown” regions that are not a promoter (3b left). This leads to suppression of transcription of tumor suppressor genes or genes that induce tumor stem cell formation, leading to drug resistance. c, EZH2 directly acts on the promoter region by itself (3c left) or with DNMTs (3c right) to methylate CpG islands in the promoter, resulting in transcriptional repression of downstream genes