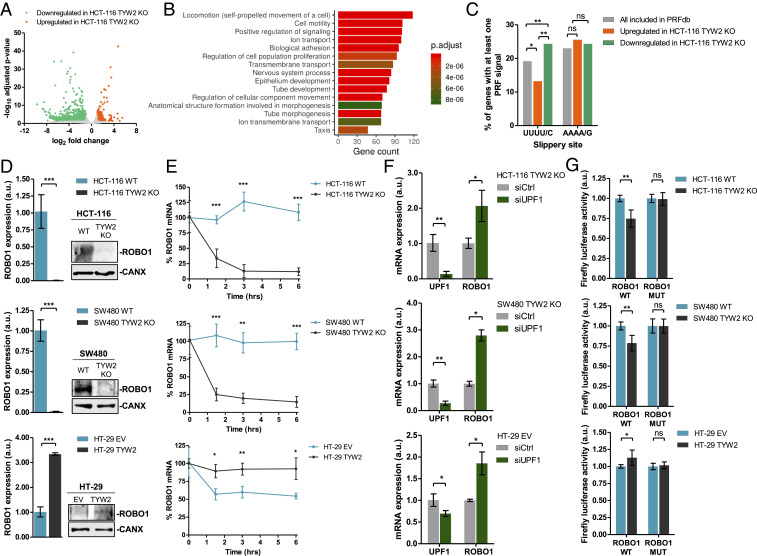
Fig. 3.
Transcriptomic identification of transcripts undergoing degradation on ribosome frameshift-mediated RNA decay and characterization of the ROBO1 candidate. (A) Volcano plot summarizing the results of the RNA-seq experiment to find differentially expressed transcripts in TYW2 CRISPR/Cas9-depleted HCT-116 cells compared with wild-type HCT-116 cells. (B) GO analysis of Biological Process categories in the transcripts down-regulated on TYW2 depletion in HCT-116 cells shows enrichment of GO Biological Process categories related to cell migration, including “locomotion,” “cell motility,” and “biological adhesion.” (C) Down-regulated transcripts in TYW2 KO cells are enriched in −1 PRF sites containing at least one UUUU/C slippery sequences that are present in tRNAPhe (Left); however, no enrichment is observed for transcripts containing AAAA/G slippery sequences, the codon for tRNALys (Right). Statistical differences among proportions were calculated using Fisher’s exact test. ns, not significant; *P < 0.05. (D) ROBO1 mRNA and protein levels in the studied experimental models. (Left) TYW2 CRISPR/Cas9 depletion in HCT-116 and SW480 cells down-regulated ROBO1 mRNA as determined by qRT-PCR. (Right) Western blot assay showing the ultimate loss of ROBO1 protein in the TYW2 KO cells. In the opposite model, TYW2 transfection-mediated recovery in HT-29 cells raised ROBO1 transcript and protein levels. For all cases, the qRT-PCR data shown represent the mean ± SD of at least three biological replicates analyzed using an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test. ***P < 0.001. (E) RNA stability determination by the actinomycin D chase assay. A reduction in ROBO1 transcripts levels is observed on CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion of TYW2 HCT-116 and SW480 cells, but not in wild-type cells. In the reverse experiment, TYW2 transfection-mediated restoration in HT-29 cells stabilized ROBO1 transcript levels. For all cases, data shown represent the mean ± SD of at least four biological replicates analyzed using the unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test at each time point. (F) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay inhibition using a siRNA against UPF1 in TYW2 CRISPR/Cas9-depleted HCT-116 and SW480 cells and in empty vector (EV) transfected HT-29 cells resulted in ROBO1 mRNA up-regulation as assessed by qRT-PCR. Data shown represents the mean ± SD of biological triplicates analyzed by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (G) In vitro assay to measure PRF events at the cloned ROBO1 mRNA containing the slippery and stimulatory sequences in the generated dual luciferase vector. HCT-116 and SW480 cells harboring CRISPR/Cas9 deletion of TYW2 showed a reduction in firefly luciferase activity compared with wild-type cells. In the reverse model, TYW2 transfection-mediated recovery in HT-29 cells increased firefly activity. No differences in firefly activity between conditions were observed when phenylalanine codons of the slippery heptamer were mutated to leucine. ROBO1 WT, wild-type phenylalanine codons; ROBO1 MUT, mutant-introduced leucine codons. P values correspond to two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.