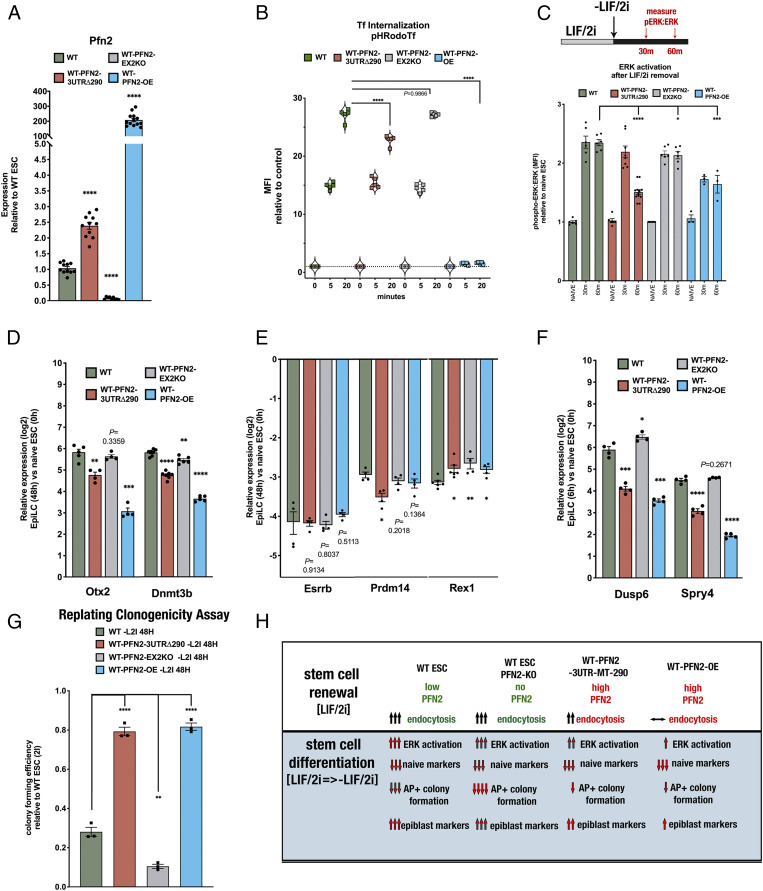
Fig. 6.
PFN2 mutants alter pluripotency transition-associated ERK activation and early differentiation in WT ESCs. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of Pfn2 expression in WT, WT-Pfn2-3UTRΔ290 mutant, WT-Pfn2-EX2KO mutant, and WT-Pfn2-OE ESCs. n = 3 independent experiments. Medium, serum + LIF/2i. Error bars represent SEM. ****P < 0.0001, unpaired two-tailed t test. (B) pH-labeled transferrin endosomal uptake assay in WT, WT-Pfn2-3UTRΔ290 mutant, WT-Pfn2-EX2KO mutant, and WT-Pfn2-OE ESCs over the indicated times, measured by the change in MFI relative to control. n = 3 independent experiments. Medium, serum+LIF/2i. Error bars represent SEM. ****P < 0.0001, unpaired two-tailed t test. (C) Intracellular phospho-ERK protein levels relative to ERK protein levels in indicated ESC samples relative to naïve conditions over the indicated time course. Statistics show comparisons at the 60 min time point after LIF/2i removal. n = 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001, unpaired two-tailed t test. (D) qRT-PCR analysis of EpiLC markers Otx2 and Dnmt3b after transition to EpiLC (at 48 h) relative to naïve state (0 h) in indicated ESC samples. n = 3 independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001, unpaired two-tailed t test. (E) qRT-PCR analysis of expression levels of naive factors Esrrb, Prdm14, and Rex1 after transition to EpiLC (at 48 h) relative to naïve state (0 h) in indicated ESC samples. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, unpaired two-tailed t test. (F) qRT-PCR analysis of expression levels of direct ERK substrates targets Dusp6 and Spry4 during transition to EpiLC (at 6 h) relative to naïve state (0 h) in indicated ESC samples. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001, unpaired two-tailed t test. (G, Top) Schematic replating assay strategy. (G, Bottom) Colony-forming efficiency assay of AP-positive ESC colonies in indicated samples. n = 3 independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM. **P < 0.01;****P < 0.0001, unpaired two-tailed t test. (H) Summary schematic reviewing effects of Pfn2 mutant ESCs in stem cell renewal and early pluripotency transition.