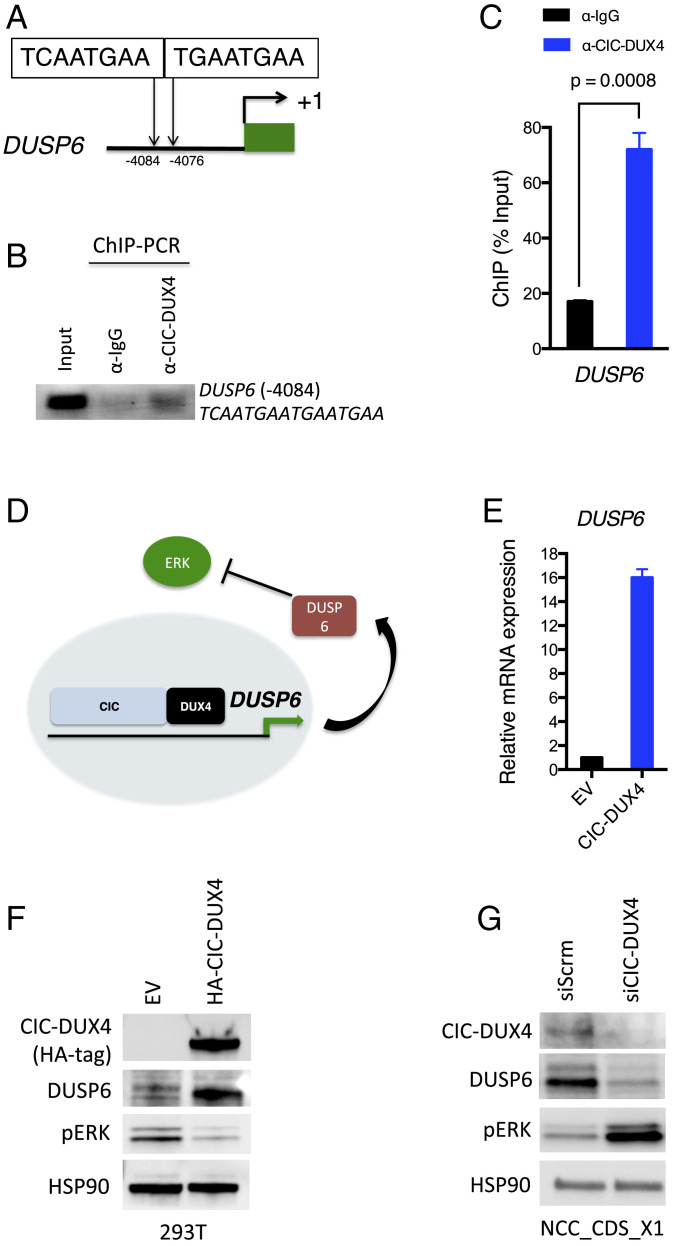
Fig. 3.
DUSP6 is a direct transcriptional target of the CIC-DUX4 fusion oncoprotein. (A). Putative tandem CIC canonical binding sites (−4,084 ∼ −4,076 bp to the TSS) in the DUSP6 regulatory domain. (B and C) ChIP-PCR demonstrating CIC-DUX4 occupancy in the regulatory region of the DUSP6 gene. IgG antibody pulldown served as a negative control (B), and the quantification of ChIP-PCR–amplified DNA bands was normalized to input DNA (C). P values were calculated using Student’s t test. Error bars indicate SEM. (D) The hypothetical model of CIC-DUX4 transcriptionally up-regulates DUSP6 expression, which dampens ERK activity to sustain CIC-DUX4 expression. (E) DUSP6 mRNA expression in 293T cells expressing exogenous CIC-DUX4 compared with empty vector (EV) control. P = 0.0001, Student’s t test. Error bars indicate SEM. (F) Immunoblot of CIC-DUX4 (HA-Tag), DUSP6, and phosphorylated-ERK from 293T cells expressing CIC-DUX4 compared with EV control. (G) Immunoblot of CIC-DUX4, DUSP6, and phosphorylated-ERK from NCC_CDS_X1 (endogenous CIC-DUX4) cells with CIC-DUX4 knockdown (siCIC) compared with scramble control (siScrm).