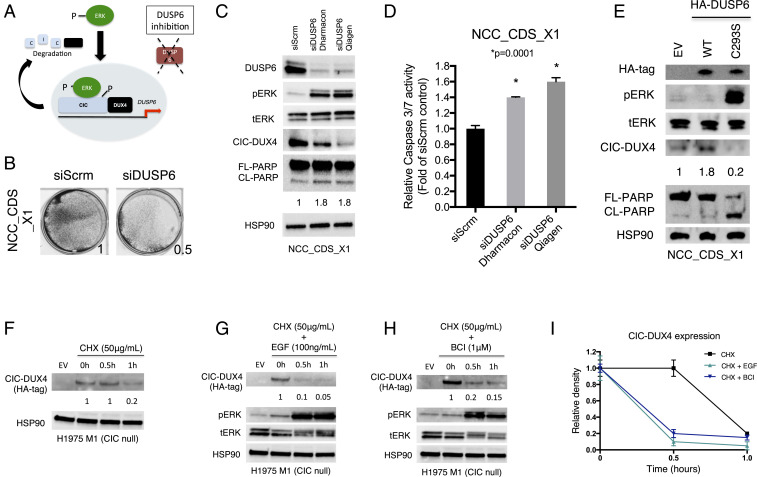
Fig. 5.
DUSP6 inhibition decreases CIC-DUX4 expression. (A) Diagram showing how DUSP6 inhibition increases ERK activity to degrade CIC-DUX4. (B) Crystal violet assay for cell viability in patient-derived CIC-DUX4–expressed sarcoma cell line NCC_CDS_X1 with either genetic inhibition of DUSP6 (siDUSP6) or scramble control (siScrm). (C) Immunoblot of NCC_CDS_X1 cells expressing siDUSP6 (Dharmacon 8), siDUSP6 (Qiagen), or scramble control. (D) Relative caspase 3/7 activity in NCC_CDS_X1 cells expressing siDUSP6 (Dharmacon 8), siDUSP6 (Qiagen), or scramble control. P values were calculated using Student’s t test. (E) Immunoblot of NCC_CDS_X1 cells expressing either HA-tagged WT DUSP6 or HA-tagged dominant negative DUSP6C293S. (F) CHX chase assay of WT CIC null cells expressing CIC-DUX4. (G) CHX chase assay of WT CIC null cells expressing CIC-DUX4 and stimulated with EGF (100 ng/mL) over the designated times. (H) CHX chase assay of WT CIC null cells expressing CIC-DUX4 and treated with DUSP6 inhibitor BCI (1 μM) over time. (I) Relative CIC-DUX4 expression comparing CHX alone, CHX + EGF, and CHX + BCI. The x-axis represent the period of indicated treatment, and the y-axis is the intensity of relative CIC-DUX4 expression. Error bars indicate SEM.