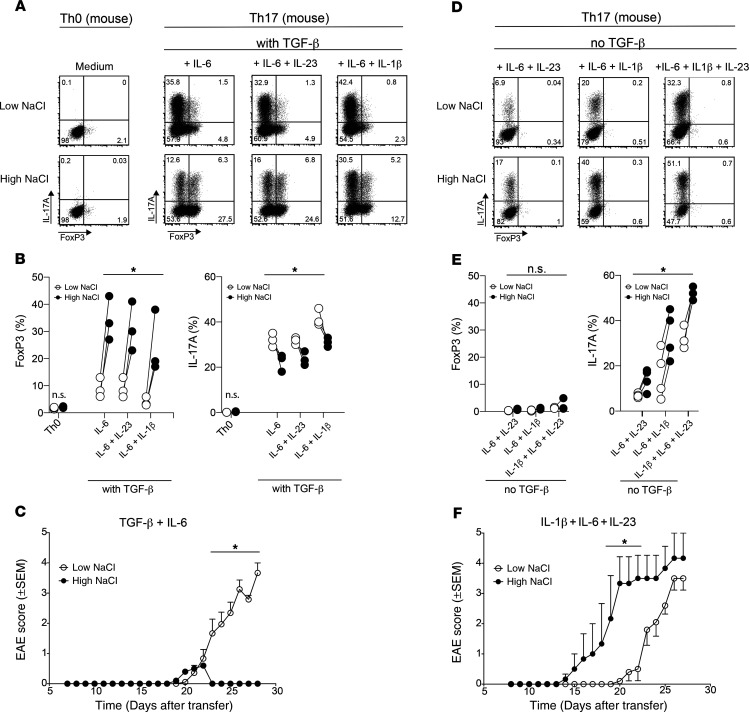
Figure 7. TGF-β governs the reciprocal enhancement of pro- versus antiinflammatory Th17 cell functions by NaCl in vitro and in vivo in an EAE mouse model.
(A) Naive murine CD4+ T cells from 2D2 mice were cultured in vitro in neutral (Th0) or various Th17-polarizing conditions (Th17), including TGF-β in low- or high-NaCl conditions, and analyzed by FACS on day 3.5 for IL-17A and FoxP3 expression. Representative dot plots show intracellular IL-17A and FoxP3 expression after restimulation of the cells with PMA and ionomycin. (B) Intracellular IL-17A and FoxP3 expression was quantified as in A. (C) Clinical EAE scores (0–5) were determined after adoptive transfer of T cells (1.5 × 106) that were polarized in vitro for 3.5 days with TGF-β and IL-6 (both 25 ng/mL) in high- or low-NaCl conditions. (D and E) Naive murine CD4+ T cells were cultured as in A in the absence of exogenous TGF-β. Representative dot plots and summary plots are shown. (F) Clinical EAE scores after adoptive transfer of T cells (2 × 106) that were polarized in vitro for 3.5 days with IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-23 in high- versus low-NaCl conditions. *P < 0.05, A 2-tailed, paired Student’s t test was performed for pairwise comparisons of low- and high-NaCl conditions (n = 3–4 mice; data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments) (B and E) and 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test (C and F).