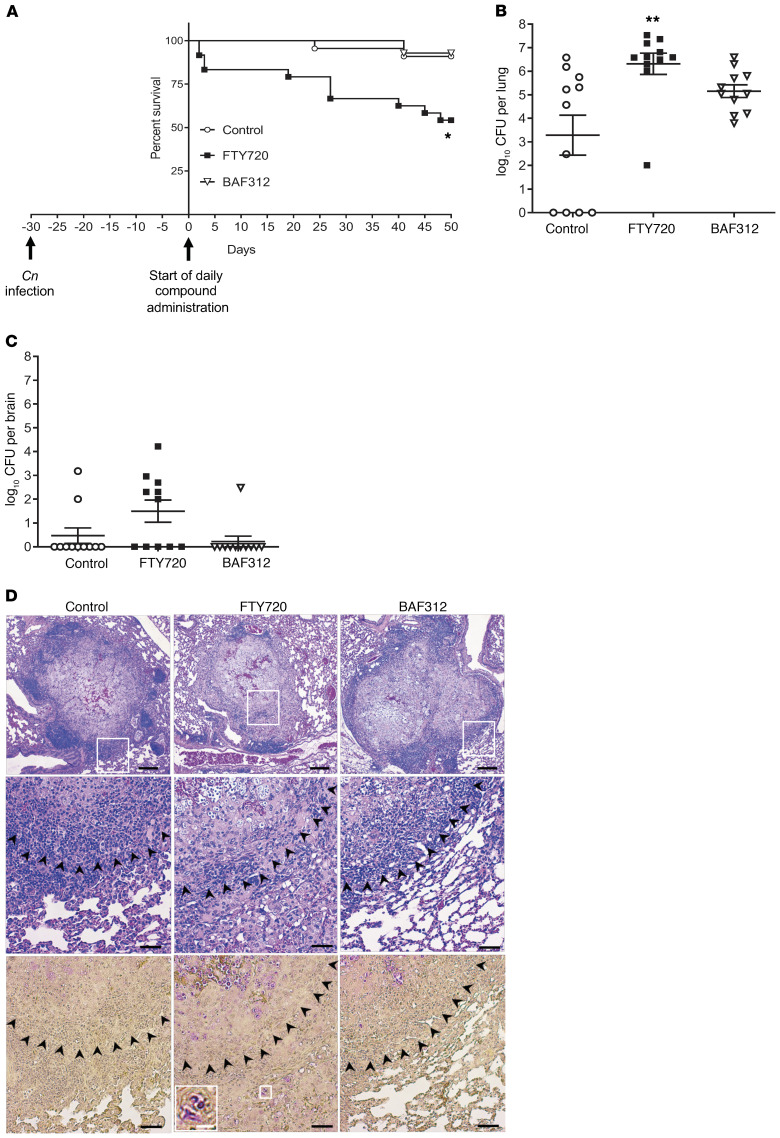
Figure 1. Mice treated with FTY720 30 days after infection have decreased survival and an increase in C.
neoformansgrowth in granulomas. (A) Mice were infected for 30 days with C. neoformans Δgcs1 before daily compound oral administration and survival of mice was monitored. All compounds were given at a dose of 1 mg/kg/day. Survival curves were compared using the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. For FTY720, n = 16 mice; BAF312, n = 14 mice; and vehicle control (H2O), n = 14 mice. *P = 0.0025. (B and C) After 50 days of daily compound administration or when mice lost more than 20% body weight, mice were sacrificed and organs were analyzed for CFUs. For FTY720, n = 11 mice; BAF312, n = 11 mice; and vehicle control (H2O), n = 11 mice. Organ burden was compared using 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons post hoc test. P values were corrected for multiplicity using the Bonferroni’s adjustment. **P = 0.0016. All error bars represent SEM. (D) After 50 days of daily compound administration, 4 lungs were isolated for histology using H&E stain (top 2 rows) and mucicarmine (bottom row). C. neoformans cells stain magenta in mucicarmine. Scale bars: 200 μm (top row), 50 μm (middle and bottom rows), and 12.5 μm (inset, white bar). The white boxes indicate the enlarged area and the black arrowheads denote the border of the granuloma.