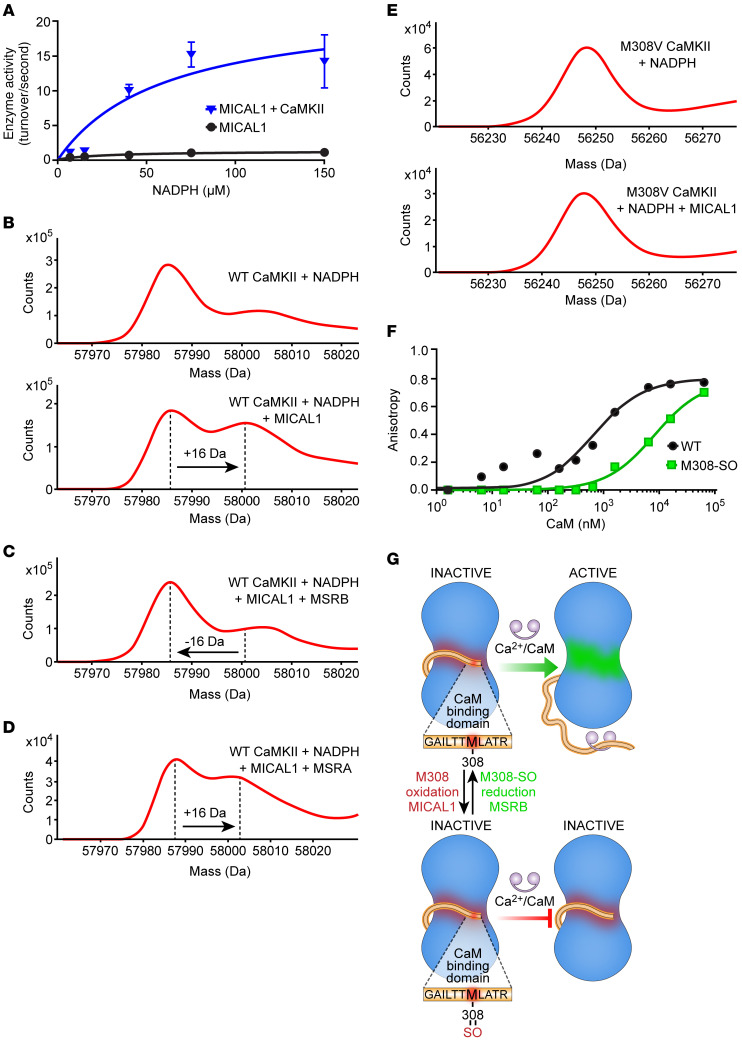
Figure 1. The redox state of CaMKII M308 is set by MICAL1 and MSRB to control CaM binding.
(A) Enzymatic activity of MICAL1 as measured by NADPH absorbance at 340 nm in the absence and presence of CaMKII with increasing concentrations of NADPH. The curves represent nonlinear regression fit derived from experimental data (curves are derived from n = 14 or 15 experimental measurements in each group; each data point represents the average of n = 2–3 measurements at different NADPH concentrations. (B) Mass spectrometry showing a +16-Da shift in the mass of WT CaMKII after incubation with MICAL1 and NADPH (bottom panel) but not with NADPH only (top panel). (C) Methionine sulfoxide reductase B (MSRB) reverses the +16-Da shift in the mass of WT CaMKII treated with MICAL1 and NADPH. (D) Methionine sulfoxide reductase A (MSRA) does not reverse the +16-Da shift in the mass of WT CaMKII treated with MICAL1 and NADPH. (E) Mass spectrometry of CaMKII M308V mutant incubated with NADPH only (top panel). CaMKII M308V mutant does not exhibit a +16-Da shift in mass after incubation with MICAL1 and NADPH (bottom panel). Findings in B–E are representative of at least 2 independent experiments. (F) Fluorescence anisotropy measurements show binding of FITC-labeled M308-sulfoxide (M308-SO) and WT peptides from CaMKII CaM-binding domain at various (n = 11) CaM concentrations. The curves represent nonlinear regression fit derived from the experimental data. Each data point represents the average of n = 2 measurements at each CaM concentration. (G) A schematic model in which the redox status of M308, set by MICAL1 and MSRB, regulates CaM binding, the requisite initial step for CaMKII activation.