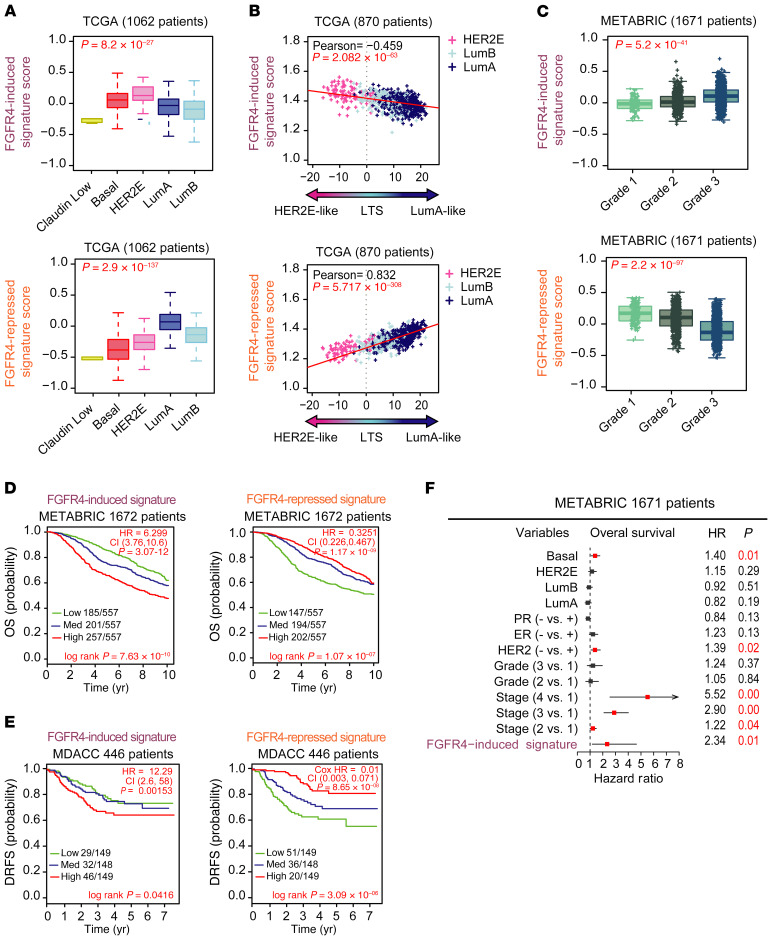
Figure 5. Prognostic value of FGFR4-derived signatures.
(A) Average expression of FGFR4-related signatures in TCGA tumor molecular subtypes. Normal-like patients and true-normal tissues have been removed from the analysis. Statistical differences were calculated by ANOVA test. (B) Scatterplot showing the correlation between FGFR4-related signatures and luminal tumor score (LTS) (as calculated in TCGA data set using only HER2E, luminal A, and luminal B tumors). Correlation was measured using the Pearson correlation coefficient. (C) Average expression of FGFR4-related signatures depending on histological tumor grade in METABRIC data (Grade 1: Low grade or well differentiated; Grade 2: Intermediate grade or moderately differentiated; Grade 3: High grade or poorly differentiated). (D and E) Kaplan-Meier plots to test the prognostic ability of FGFR4 signatures in METABRIC (D) and MDACC (E) data sets (normal-like samples were removed from the analysis in both cohorts). Survival curve differences were calculated by the log-rank test and the estimates of survival probabilities and cumulative hazard with a univariate Cox proportional hazards model. (F) Multivariable Cox proportional hazards analyses using METABRIC data (normal-like samples were removed from the analysis). Hazard ratio (HR) = 1: no effect. HR < 1: reduction in hazard. HR > 1: increase in hazard. Signatures were evaluated as continuous variables and rank ordered according to the gene FGFR4 signature scores (induced and repressed) in 3 different levels: low, medium, and high (assigned by distribution in a given upper, middle, or lower tertile). Comparison between more than 2 groups was performed by ANOVA. Statistically significant values are highlighted in red. Box-and-whisker plots display the median value on each bar, showing the lower and upper quartile range of the data and data outliers. The whiskers represent the interquartile range. Each mark represents the value of a single sample. LumA, luminal A; LumB, luminal B.