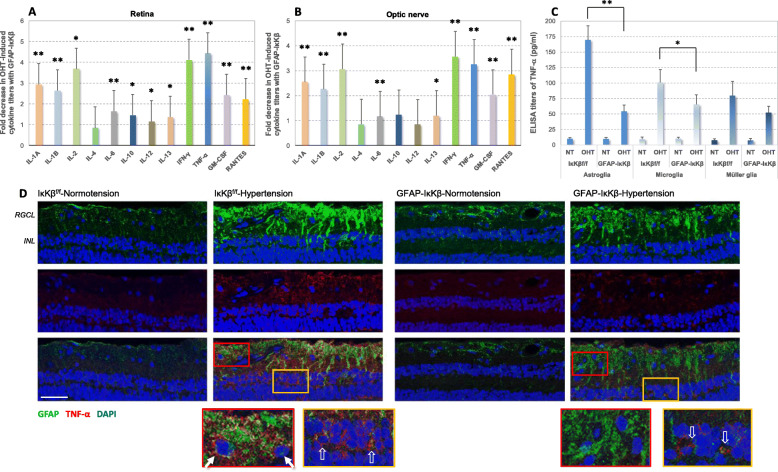
Fig. 3.
Effects of astroglial IκKβ deletion on neuroinflammatory responses of the ocular hypertensive mouse retina. In order to determine the inflammatory status of retina (a) and optic nerve (b) tissues, cytokine titers were analyzed by ELISA. We detected significantly reduced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in ocular hypertensive GFAP-IκKβ eyes compared to ocular hypertensive controls (IκKβf/f mice wild-type for cre). Bar graphs show fold decrease in ocular hypertension (OHT)-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine production with GFAP-IκKβ. Data (mean ± SD) from retina and optic nerve samples are presented by separate graphs (represents a minimum of 4 mice per group; **P < 0.001, *P < 0.05). c Isolated samples of retinal astroglia and microglia (by immunomagnetic cell selection) also presented reduced titers of TNF-α (a major pro-inflammatory cytokine relevant to glaucomatous neurodegeneration) in ocular hypertensive GFAP-IκKβ than ocular hypertensive IκKβf/f controls. However, there was no significant difference between the TNF-α titers in normotensive (NT) samples from GFAP-IκKβ or IκKβf/f mice (P > 0.05). Reduced production of TNF-α with GFAP-IκKβ was more significant in astroglia (**P < 0.001) than microglia (*P = 0.02). When the isolated samples of retinal Müller glia were similarly analyzed, no significant difference was detectable in the ocular hypertension-induced TNF-α production of Müller glia between GFAP-IκKβ mice and IκKβf/f controls (P = 0.06). d Astroglial pro-inflammatory phenotype was also studied by immunohistochemical analysis. Presented are TNF-α immunolabeling of retinal tissue sections (scale bar, 100 μm), and red or yellow boxed areas are shown in higher magnification. TNF-α immunolabeling (red) of GFAP+ astroglia (green) was prominently higher in ocular hypertensive IκKβf/f retina (white arrows) than normotensive controls. However, astroglial TNF-α immunolabeling was not detectable in the RGC layer (corresponding to astrocytes), but still detectable in the inner nuclear layer (corresponding to Müller glia; translucent arrows) of ocular hypertensive GFAP-IκKβ retinas. Blue indicates nuclear DAPI staining. RGCL, and INL mark retinal ganglion cells layer, and inner nuclear layer, respectively