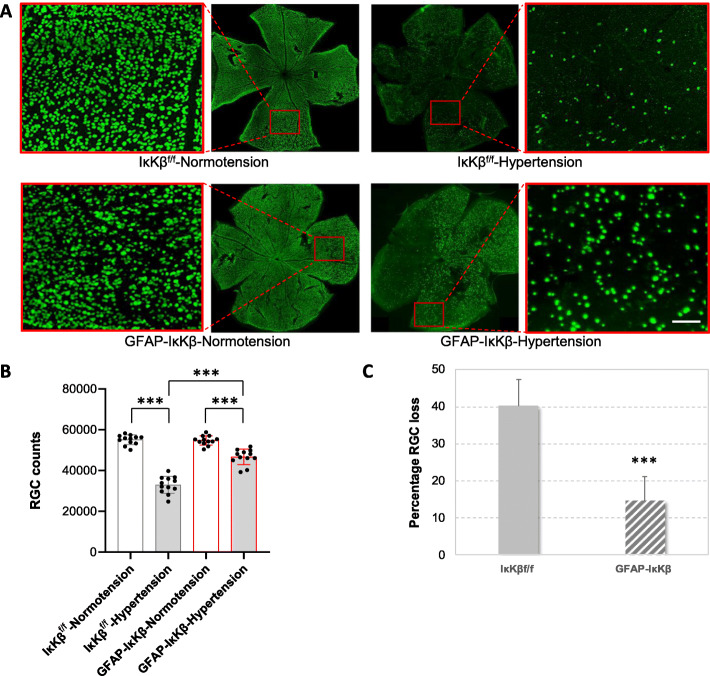
Fig. 5.
Transgenic effects on RGC counts. a Composite images of the whole-mounted retinas immunolabeled for RPBMS, an RGC marker. Red boxed areas are shown in higher magnification (scale bar, 100 μm). Ocular hypertensive control eyes (IκKβf/f mice wild-type for cre) exhibited a visible loss of RPBMS-labeled RGC somas compared to normotensives; however, RGC bodies were well protected in ocular hypertensive eyes of GFAP-IκKβ mice. RPBMS-labeled RGC somas were counted and the neuron loss was determined in ocular hypertensive eyes after adjusting to normotensive fellow eyes. The number of RPBMS-labeled RGCs was significantly higher in ocular hypertensive GFAP-IκKβ retinas than ocular hypertensive IκKβf/f controls (***P < 0.001). Bar graphs in panel b present RGC counts in GFAP-IκKβ mice and IκKβf/f controls with or without experimentally induced ocular hypertension, and bar graphs in panel c show percentage of RGC loss in ocular hypertensive transgenic or control animals. Presented data (mean ± SD) represents a minimum of 16 mice per group. Transgenic deletion of astroglial IκKβ resulted in an approximately 63% protection of RGC somas in ocular hypertensive eyes