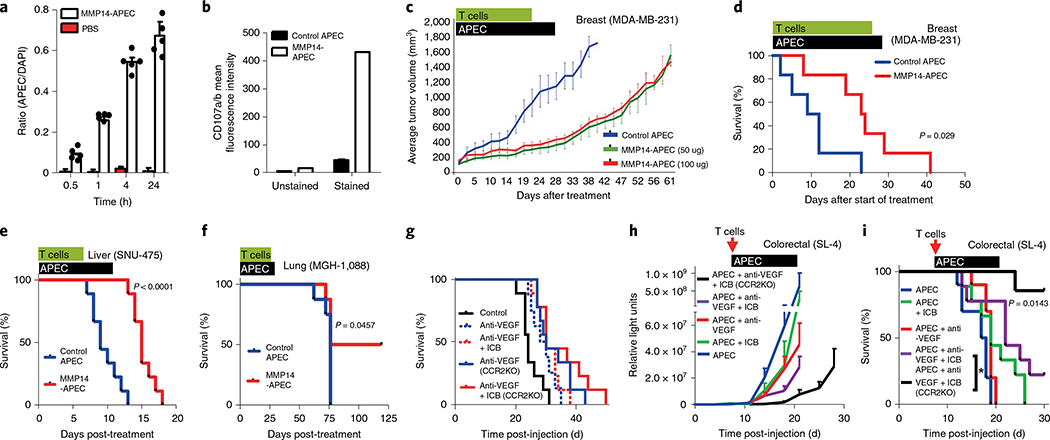
Fig. 3 |. APEC modulation of antigenicity in vivo.
a, In vivo tumor penetration of APEC-treated NOD/SCID mouse model of primary orthotopic human breast cancer (MDA-MB-231) using the ratio of APEC to DAPI (n = 4 independent samples). Data shown as mean and error bars represent s.d. b, In vivo T-cell cytotoxic capacity, as assayed by CD107 staining, demonstrated increased cytotoxic activity of freshly isolated CMV-CTL in MDA-MB-231 treated with MMP14-cAPEC compared with control cAPEC. c, NOD/SCID mouse model MDA-MB-231 (n = 8) demonstrated a delay in tumor growth following treatment with 50 μg or 100 μg MMP14 cAPEC compared with control cAPEC. d, MMP14-cAPEC improved the survival of mice (n = 8) in a breast cancer neoadjuvant model compared with control cAPEC (P = 0.029, Mantel-Cox two-sided test) after injection of ex vivo expanded CMV-CTL. e, Survival of mice orthotopically injected with hepatocellular carcinoma cell line SNU-475 (n = 8) treated with MMP14-cAPEC and ex vivo expanded CMV-CTL was improved compared to that of mice treated with control cAPEC (P< 0.0001, Mantel-Cox two-sided test). f, Improved survival of mice (n = 5) treated subcutaneously with MMP14 or control cAPEC and ex vivo expanded CMV-CTL in a PDX model of lung cancer (P = 0.0457, Mantel-Cox two-sided test). g, C57BL/6 or Ccr2−/− (C57 background) mouse model (n = 10) of metastatic colorectal carcinoma (SL4 clone) demonstrated only a marginal increase in survival when treated with either anti-VEGF or anti-VEGF in combination with ICB therapy (anti-PD-1+ anti-CTLA-4). All mice received ex vivo expanded OT-I T cells specific for SIINFEKL. h,i, Ccr2−/− mice (n = 8–10) treated with combination immune checkpoint blockade (therapy of anti-VEGF+ ICB+ murine APEC system demonstrated significant delay in tumor growth (h) and increased survival (i) compared with wild-type mice treated with the same reagents or with other APEC combination therapies (P = 0.0143, Mantel-Cox two-sided test). All mice received ex vivo expanded OT-I T cells specific for SIINFEKL. In relevant panels, error bars represent s.e.m.