Figure 4. Nerve injury-induced latent pain sensitization requires spinal AC1.
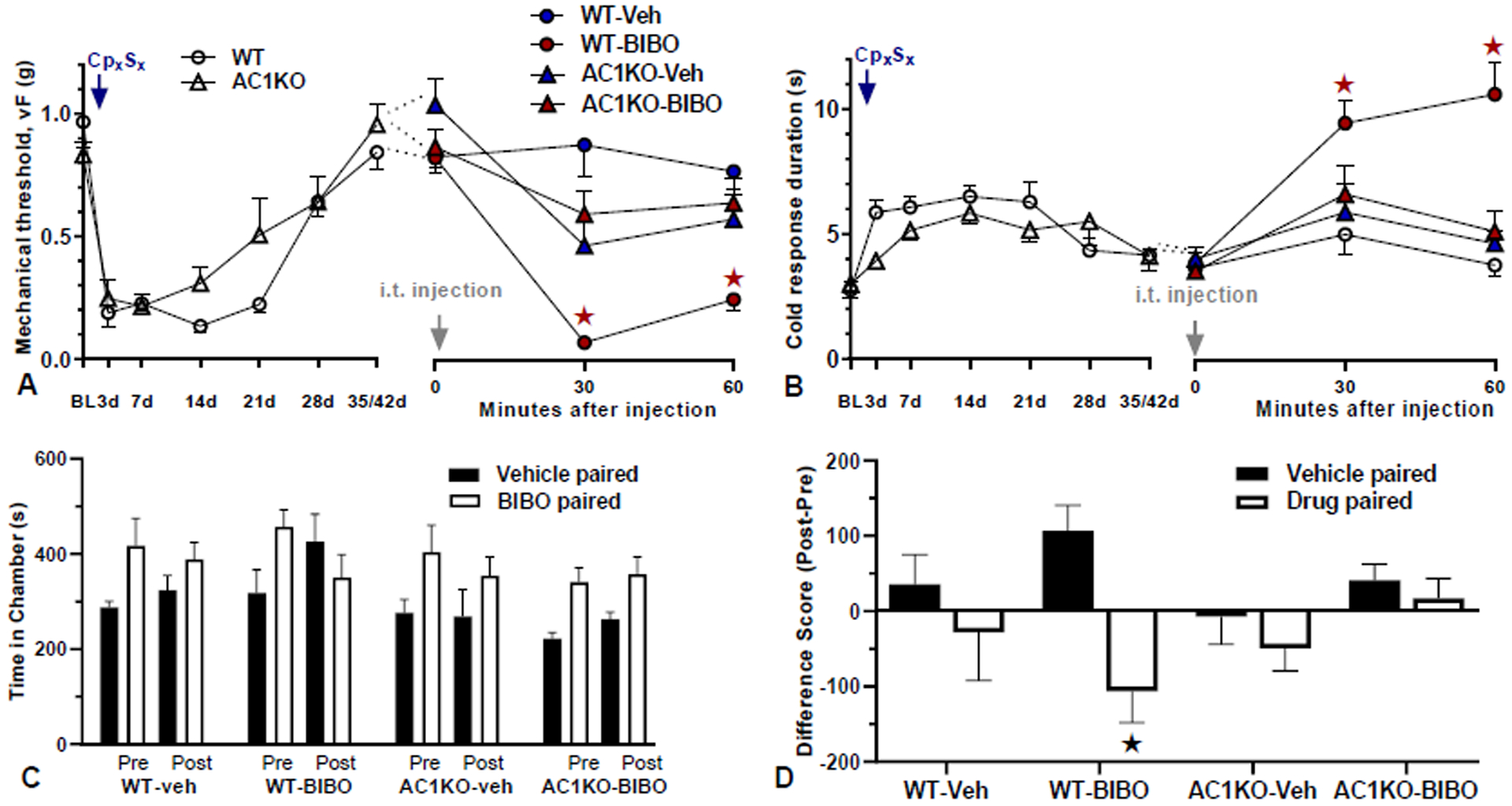
A–B) Time course of mechanical (A) and cold (B) thresholds in AC1KO mice and their WT littermates at pre-surgery baseline, d3, d28 after CpxSx surgery, and 30 and 60 min after intrathecal (i.t.) injection. A–B, Left) Progression and resolution of CpxSx-induced mechanical and cold hypersensitivity. n=11 (AC1KO); n=12 (WT). ★P < 0.05. A–B, Right) During pain remission 28–35 days after CpxSx surgery, BIBO3304 (BIBO, 5 μg/5 μl) or vehicle was injected. All animals were injected twice using a cross-over design with 7-day separation between the two i.t. injections. Post-injection n=12 (WT-Veh); n=12 (WT-BIBO); n=13 (AC1KO-Veh); n=13 (AC1KO-BIBO). ★P < 0.05 (AC1KO-BIBO vs WT-BIBO). C) time spent in side chambers during the preconditioning and postconditioning test phases of a CPA assay conducted 40–43 days after CpxSx surgery. D) difference score of postconditioning minus preconditioning values. BIBO3304 produces place aversion in WT but not AC1KO mice. n=4–6 per group, ★P < 0.05 (WT-BIBO: vehicle vs drug chamber). Values represent mean ± SEM.
