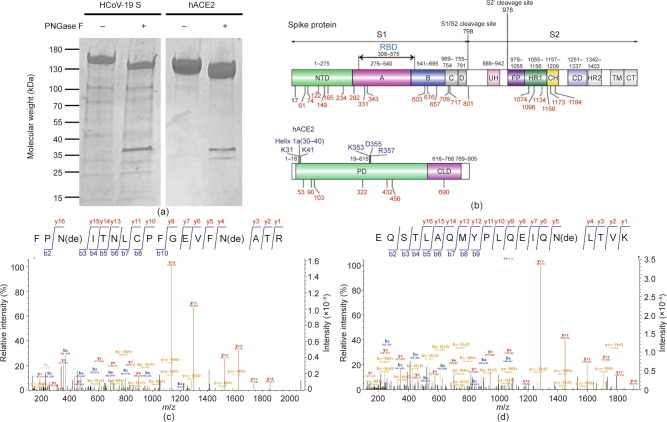
Fig. 1.
Potential glycosylation sites in the HCoV-19 S protein and hACE2. (a) 15% SDS-PAGE analysis of the intact and deglycosylated form of the HCoV-19 S protein and hACE2. Molecular weight markers are shown on the left. (b) Schematic representation of the functional subunits and domains of the HCoV-19 S protein (upper panel) and hACE2 (lower panel). CD: connector domain; CH: central helix; CT: cytoplasmic tail; FP: fusion peptide; TM: transmembrane domain; UH: upstream helix; HR1/2: heptad repeat 1/2. Blue indicates the domain or amino acids possibly responsible for interaction between the S protein and hACE2. Potential glycosylation sites within each domain are indicated. Red marks represent identified glycosylated sites in this study. (c, d) Mass spectra of deglycosylated peptide containing (c) N331 and N343 in the HCoV-19 S protein and (d) N90 in hACE2. NTD: N-terminal domain; PD: peptidase domain; CLD: C-terminal collectrin-like domain; de: deamidation.