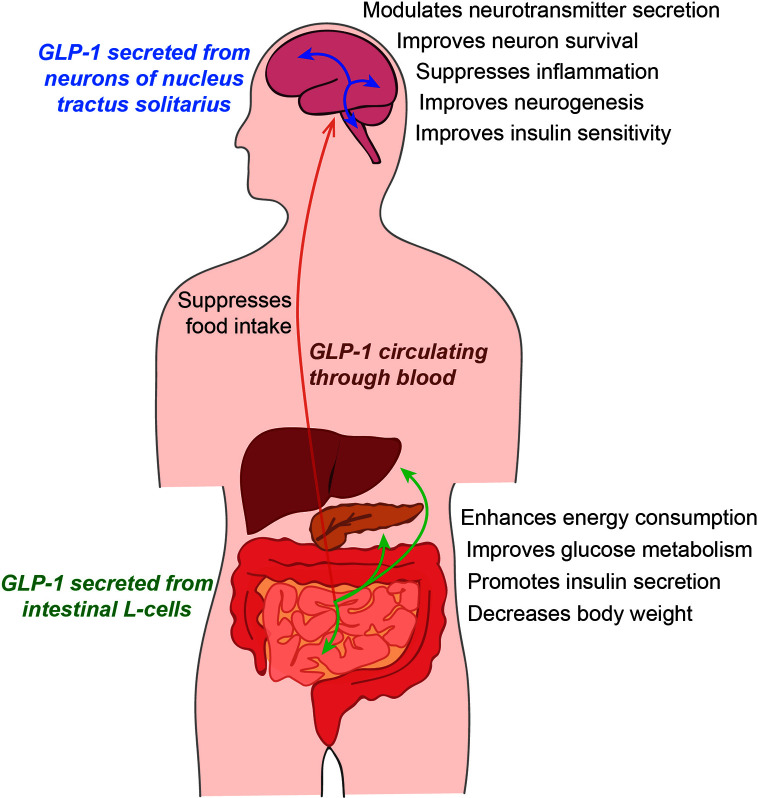
Figure 1.
The function of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) in humans. GLP-1, secreted from the intestinal L-cells, circulates the whole body through the blood. GLP-1 influences energy metabolism and glucose metabolism by regulating the insulin level. In the brain, GLP-1 secreted from intestinal cells can be absorbed into the brain, and the GLP-1 secreted from neurons remains in the cerebrospinal fluid. GLP-1 can control the secretion of various neurotransmitters and the progression of neuroinflammation, and can regulate insulin sensitivity in the brain.