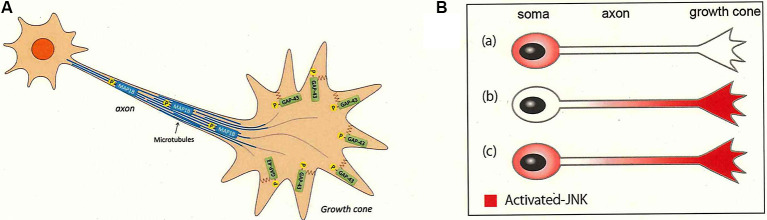
Figure 4.
JNK activity in the axon and its substrates for axonal growth. JNK is activated in the developing neurons (Hirai et al., 2011; Yamasaki et al., 2011; Coffey, 2014). (A) JNK-dependent substrates are sorted to the distal axon and the growth cone. Phosphorylated segments of GAP-43 (peptides pS96 and pT172) and MAP1B (peptides pS25 and pS1201) are sorted to the plasma membrane and the microtubules in the growth cone of the distal axon, respectively. These substrate proteins are phosphorylated by JNK in the cell bodies before undergoing anterograde axonal transport or are phosphorylated by JNK proximal to the growth cone area [see (A)]. See Kawasaki et al. (2018) and Ishikawa et al. (2019). (B) JNK may be distributed within the growing axons in one of three patterns: (Ba) only in the cell bodies, (Bb) only in the growth cone, or (Bc) in the whole neuron. Our experimental results indicate that (Ba) or (Bc) are more likely (Kawasaki et al., 2018).