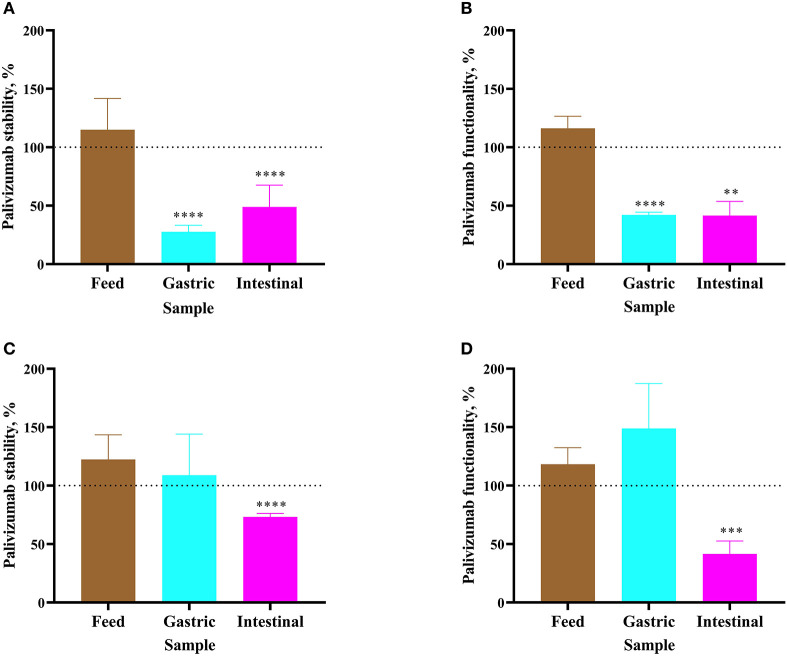
Figure 2.
Stability of palivizumab during a 1 h ex vivo digestion in feed (brown bars), gastric samples (cyan) and intestinal samples (magenta) in (A) Infant 1 and (C) Infant 2, respectively, tested by anti-idiotype ELISA and represented as percentage of the original palivizumab content. Stability of palivizumab neutralization capacity across ex vivo digestion in the sample from (B) Infant 1 and (D) Infant 2 based on NT50 and represented as a percentage of the original functionality. Values are mean ± SD, n = 6 and 3 dilutions for Infants 1 and 2, respectively, measured in triplicate for ELISA and n = 3 experimental replicates measured in duplicate for the RSV neutralization assay. Asterisks show statistically significant differences (**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; and ****P < 0.0001) between time 0 and 1 h of incubation within each sample type using unpaired t-tests. The broken line shows palivizumab stability in the anti-idiotype ELISA and palivizumab functionality in the RSV neutralization assay in feed (0 h), gastric (0 h), and intestinal (0 h) as 100%.