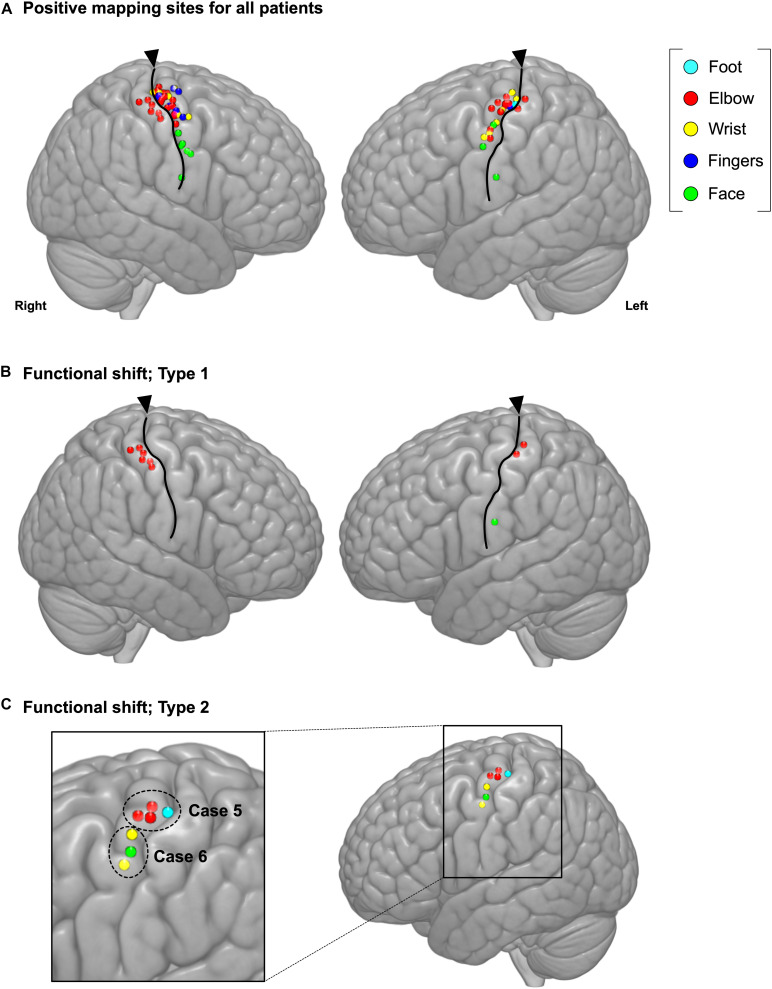
FIGURE 2.
Positive mapping of motor function sites during awake surgery. (A) The cerebral regions were directly stimulated during awake surgery to identify the motor area. When involuntary movement or dystonic movement was observed (positive mapping), these regions were defined as the motor area. We marked the location of positive mapping sites and body parts for which the symptoms were elicited. Upon analyzing the characteristics of the motor area’s functional shift, we identified two functional shift types: (B) Type 1 (move to ipsilateral different gyrus) and (C) Type 2 (move within the ipsilateral precentral gyrus). Cyan: foot; red: elbow; yellow: wrist; blue: fingers; green: face; triangles: location of central sulcus.