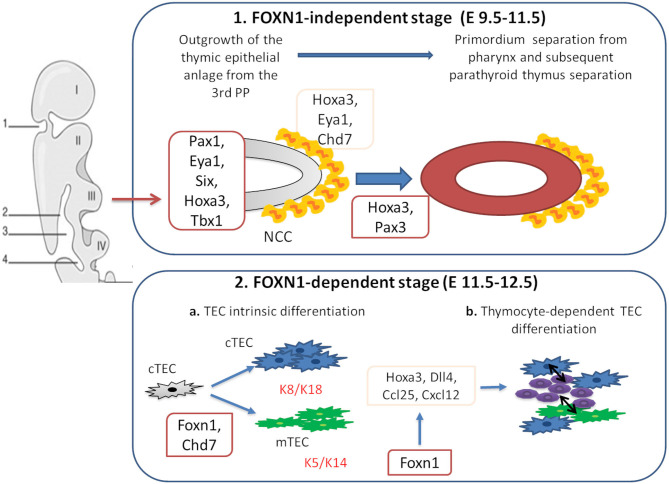
Figure 1.
Genes involved in thymus organogenesis. Eya1, Six, Hoxa3, Tbx1, and Chd7 take part to the first stages of thymus development from neural crest cells (NCCs) in the posterior part of the 3rd pharyngeal pouch (PP). This step is independent from Foxn1 expression. In the second stage, Foxn1 regulates the expression of Hoxa3, Dll4, Ccl25, and Cxcl12, necessary for the thymic epithelial cells (TECs) differentiation. During this phase, cTECs (expressing K8 and K18 keratin type) and mTECs (expressing K5 and K14 keratin type) originate from the same bi-potential TECs progenitor. Chd7 is also critical for the development of cortical and medullary TECs from pharyngeal endoderm. The crosstalk between TECs and developing thymocytes is required to generate mature TECs and functional T cells.