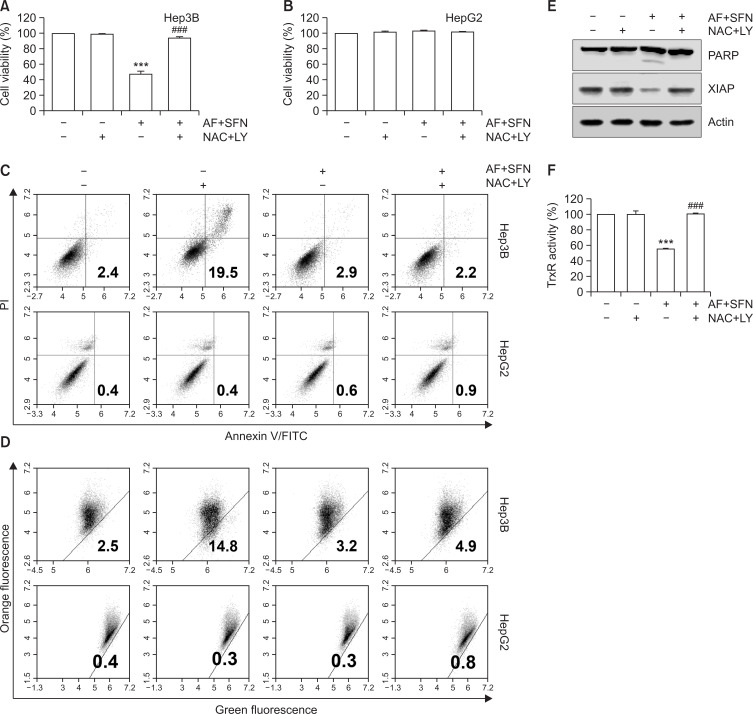
Fig. 9.
ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling pathway modulated combined treatment-induced apoptosis in Hep3B cells. The cells were pretreated with NAC (10 mM) and LY294002 (5 μM) for 1 h prior to combined treatment with auranofin (AF) (1 μM) and sulforaphane (SFN) (7.5 μM). (A, B) Cell viability and TrxR activity were measured by MTT assay and DTNB reduction assay, respectively. The error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments. *** indicates significant differences at p<0.001, compared to the control group; ### indicates significant differences at p<0.001, compared to auranofin and sulforaphane-treated group. (C) Following treatment, the cells were stained with annexin-V/PI and analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) MMP was measured by JC-1 staining and analyzed flow cytometry. (E) Alterations in apoptosis-related protein expression were analyzed by Western blotting. Total cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE, and the proteins were transferred to membranes. Each membrane was reacted with the indicated antibodies against apoptosis-related proteins. Actin served as a control for equal loading. (F) TrxR activity was measured by DTNB reduction assay. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. The error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments. *** indicates significant differences at p<0.001, compared to the control group, ### indicates significant differences at p<0.001, compared to auranofin and sulforaphane-treated group.