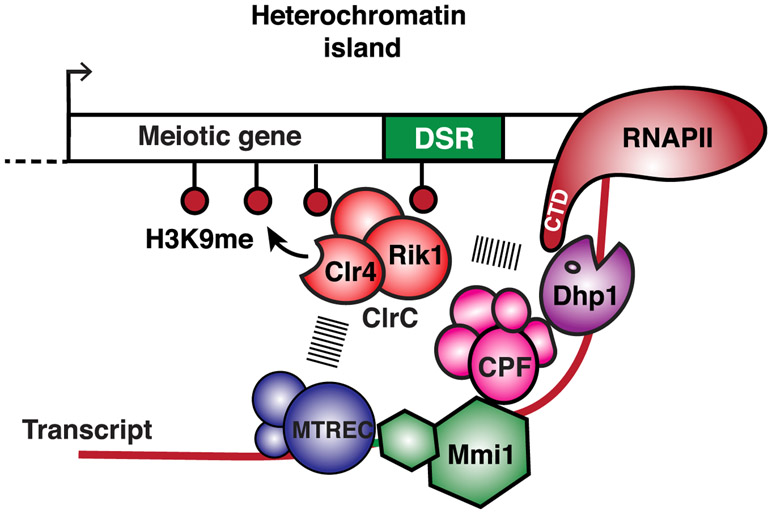
Figure 7. Model Showing Facultative Heterochromatin Assembly and Gene Silencing by Transcription Termination and RNA Degradation Factors.
Mmi1 binds target transcripts and recruits factors involved in RNA decay, such as MTREC, as well as 3′ end processing and transcription termination factors, such as CPF, to couple non-canonical termination of RNAPII with RNA degradation and recruitment of heterochromatin assembly factors. RNA cleavage by CPF and other factors may provide an entry site for MTREC to prepare transcripts for degradation by the 3′ →5′ exoribonuclease activity of the nuclear exosome Rrp6 (not shown) and by 5′ → 3′ exoribonuclease Dhp1XRN2, required for RNAPII termination. RNA degradation factors, in particular MTREC, and termination proteins, including Dhp1XRN2, recruit the Clr4SUV39H -containing ClrC complex to trigger RNAi-independent heterochromatin assembly. The ClrC subunit Rik1, which has similarity to a CPSF subunit and is loaded concomitantly with RNAPII transcription of target loci (Zhang et al., 2008), likely plays an important role in linking termination and degradation factors to the recruitment of Clr4 SUV39H.