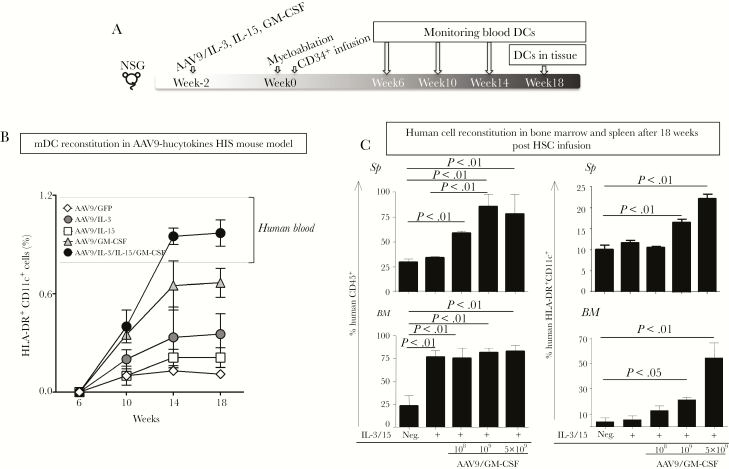
Figure 1.
Reconstitution of human myeloid cells in human immune system (HIS) mice. (A) Experimental scheme to generate adeno-associated virus serotype 9 (AAV9)-hucytokines HIS mice. Recombinant AAV9 (rAAV9) vectors that encode human interleukin (IL)-3, IL-15, or granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) were administered separately, or in combination, to 2-week-old NOD/SCID/IL2Rgammanull (NSG) mice. Recombinant rAAV9 encoding for green fluorescent protein was used as a mock control. Two weeks later, mice were sublethally irradiated for myeloablation, and 24 hours later, purified human CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) were intravenously injected into mice. Reconstitution of human CD45+ cells, as well as myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs), in blood and in tissues was monitored at 6, 10, 14, and 18 weeks post-HSC infusion. (B) For monitoring DCs, mouse CD45− human CD45+ (mCD45−hCD45+) cells were gated on Lin− (CD3, CD14, CD16, and CD19) and evaluated for expression of human CD11c and human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR. The percentage of HLA-DR+CD11c+ DCs are displayed 6, 10, 14, and 18 weeks after the HSC infusion using line graphs with symbols representing the mean values and standard error lines. Dashed lines represent the minimum and maximum values for HLA-DR+CD11c+ DCs in human blood as reference for DC humanization. (C) Different doses, 108, 109, or 5 × 109 genomic copies, of rAAV9 that encodes 1 or all of human cytokines were injected into each NSG mouse, followed by HSC infusion. These mice were monitored for reconstitution of human CD45+ cells, as well as HLA-DR+CD11c+ DCs in bone marrow (BM) and spleen. Experiments included 3–5 mice per group and were repeated 4 times. Results illustrate data from 1 representative experiment (n = 5). Statistical analyses were performed using analysis of variance followed by Dunnett’s test and differences were considered if P < .05.