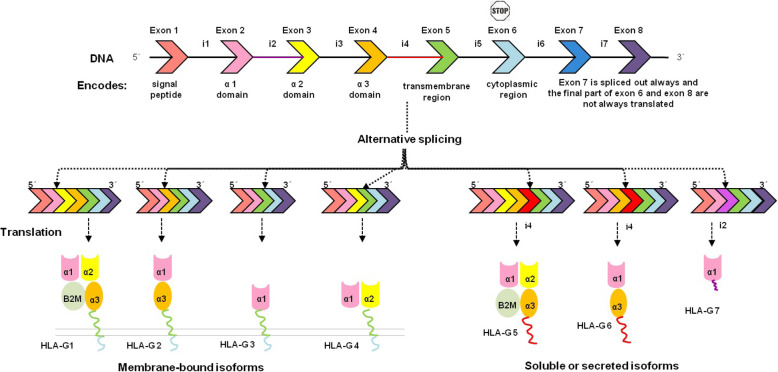
Fig. 1.
HLA-G heavy chain gene comprises 7 introns (i1-i7) and 8 exons (each with a distinctive color) with an internal stop codon in Exon 6. As shown in figure each exon encodes a discrete part of the heavy chain, except exon 7 and 8. Alternative splicing events of HLA-G primary transcript (exclusion exon 3 or/and exon 4 and keeping of intron 4 or intron 2 from the final gene transcript) generate seven isoforms. Soluble isoforms lack the transmembrane and cytoplasmic regions due to the intron retention, which includes an immature stop codon. HLA-G5 and HLA-G6 have a tail (21 amino acids) that plays a role in their solubility. HLA-G1 is the complete molecule. HLAG1 is homologous to HLA-G5 and both of them associate with B2M. The signal peptide (exon 1) and α1 domain (exon 2) are existing in all isoforms. Figure modified from Bainbridge et al. [14]