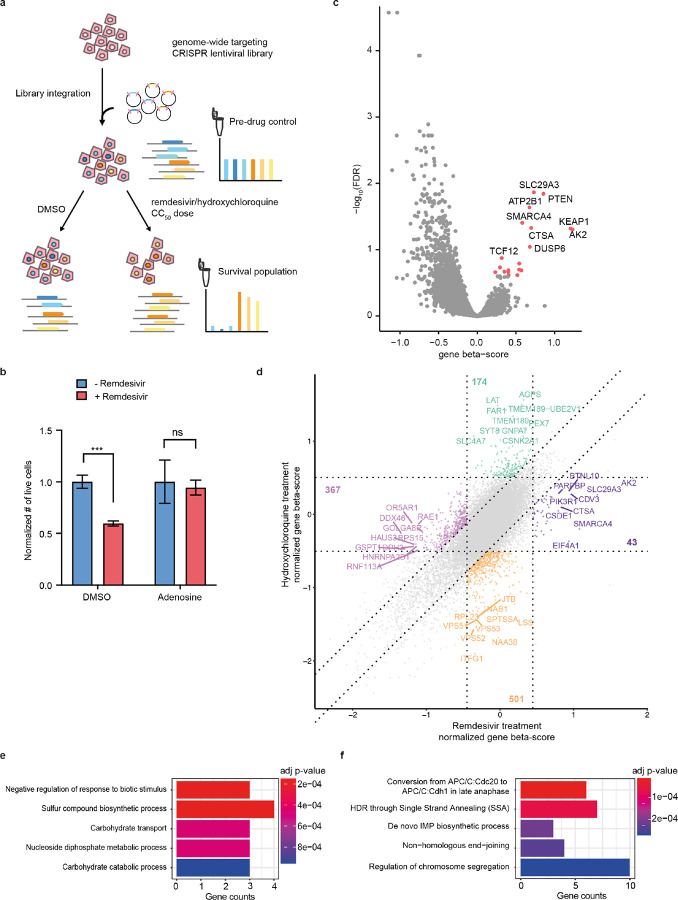
Figure 2. A drug toxicity CRISPR-Cas9 screen identifies candidate genes and pathways involved in the mitigation and exacerbation of remdesivir cytotoxicity.
a) Schematic of pooled CRISPR screen. Cells were transduced with Brunello lentiviral library and treated either with DMSO or for 14 days with doses of remdesivir or HCQ titrated to yield 50% surviving cells every five days of treatment. Genomic DNA was collected before and after drug for sequencing of gRNA abundance. b) Effect on remdesivir toxicity of 100-fold molar excess of adenosine in HT29 cells. Error bars are SE. c) Volcano plot showing beta score calculated for the 4 gRNAs targeting each gene vs. the −log10(FDR) of remdesivir treatment vs. DMSO treatment across 6 screening replicates. d) Square plot showing normalized gene beta score normalized to pre-drug control for remdesivir vs. HCQ treatment. e-f) Top 5 most significant GO terms enriched (e) and depleted (f) after remdesivir treatment vs. DMSO treatment.