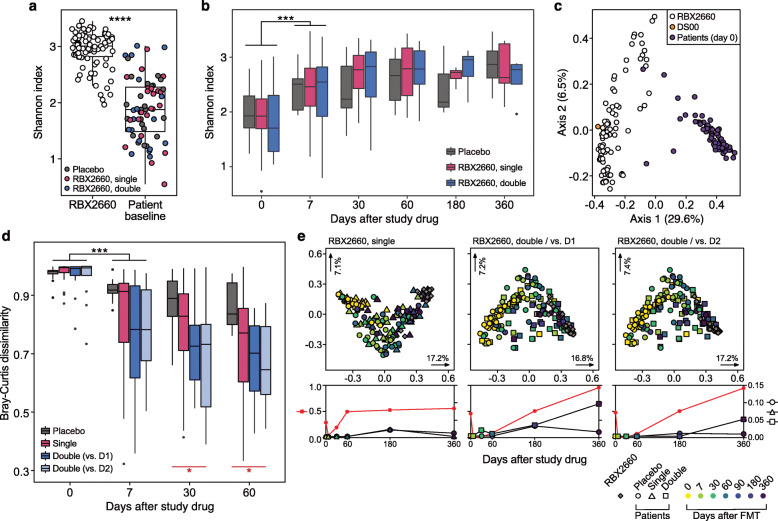
Fig. 2.
RBX2660 shifted taxonomic structures of the gut microbiome of recipients toward a healthy state. a RBX2660 products exhibited significantly higher alpha diversity than patient samples before treatment (Wilcoxon signed-rank test) based on the metagenomic taxonomic profiling data. b Alpha diversity of all patients including placebo recipients increased similarly after treatment. Changes in alpha diversity were significant for the first week after treatment, but there was no statistically significant difference among treatment groups (Kruskal-Wallis test). c Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) showed a species-level clustering of RBX2660 (white) and pseudo-donor sample DS00 (yellow) distinct from patient baseline samples (violet). d Bray-Curtis distance between taxonomic structures of patients and corresponding RBX2660. D1 and D2 indicate the first dose and the second dose, respectively. DS00 was used for calculating the Bray-Curtis distance of placebo recipients. The decrease in Bray-Curtis distances was steepest during the first week after treatment (black, Wilcoxon signed-rank test). RBX2660 recipients showed a more dynamic decrease in Bray-Curtis distances than placebo recipients by day 60 (red, Kruskal-Wallis test). *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001. e Upper panels: PCoA describing the direction of changes in taxonomic structures of RBX2660 recipients. Corresponding RBX2660 products and all placebo recipients were included. Lower panels: adjusted P values of PERMANOVA and relevant pairwise comparisons (Pillai-Bartlett non-parametric trace and Benjamini-Hochberg FDR correction). P values of comparisons between placebo and RBX2660 recipients (red asterisks, left y-axis), placebo recipients and RBX2660 (circle, right y-axis), single-dose recipients and RBX2660 (triangle, right y-axis), and double-dose recipients and RBX2660 (square, right y-axis) of PCoA plots were presented in corresponding lower panels