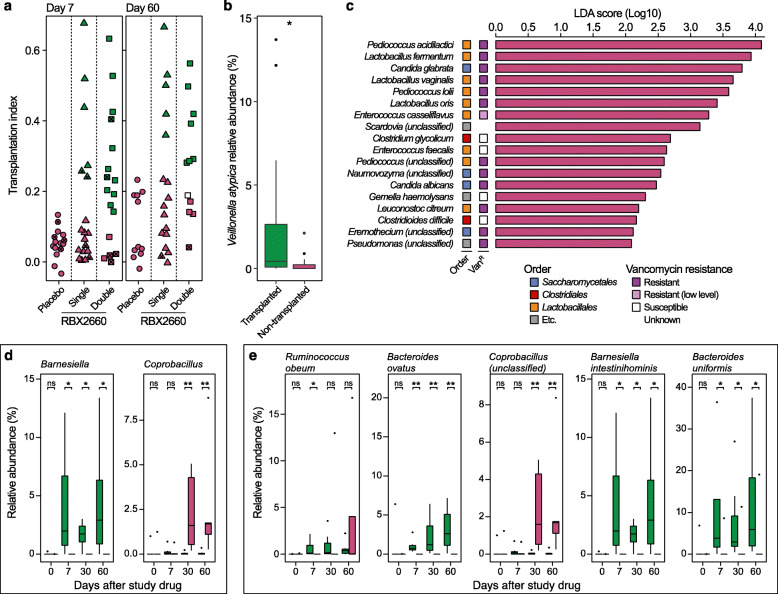
Fig. 3.
Discriminative taxonomic features of RBX2660 transplantation. a Transplantation index of patients on day 7 and 60. We defined the taxonomic transplantation as a state showing a higher transplantation index than that of all placebo recipients (green). The patients who were declared rCDI within 60 days were marked (x). The white square represents the patient who exhibited a lower transplantation index for the first dose but a higher transplantation index for the second dose than placebo patients (R2-21, Fig. S7a). b Higher baseline relative abundances of Veillonella atypica in patients who showed durable taxonomic transplantation by day 60 in both single and double RBX2660 treatment groups (Wilcoxon signed-rank test, P = 0.027). c Linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe) determined baseline taxonomic features of the obstinate non-transplanted patients who exhibited lower transplantation indices than placebo recipients at day 60 after double RBX2660 treatment. Thirteen species among 18 taxonomic features were intrinsically vancomycin resistant (violet square, including E. casseliflavus of low resistance). There was no taxonomic feature specific to transplanted patients determined by LEfSe. Genus (d) and species enrichment (e) associated with the taxonomic transplantation (transplanted, green; non-transplanted, purple) were identified through a two-part zero-inflated Beta regression model with random effects (ZIBR) test. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01