Fig. 6.
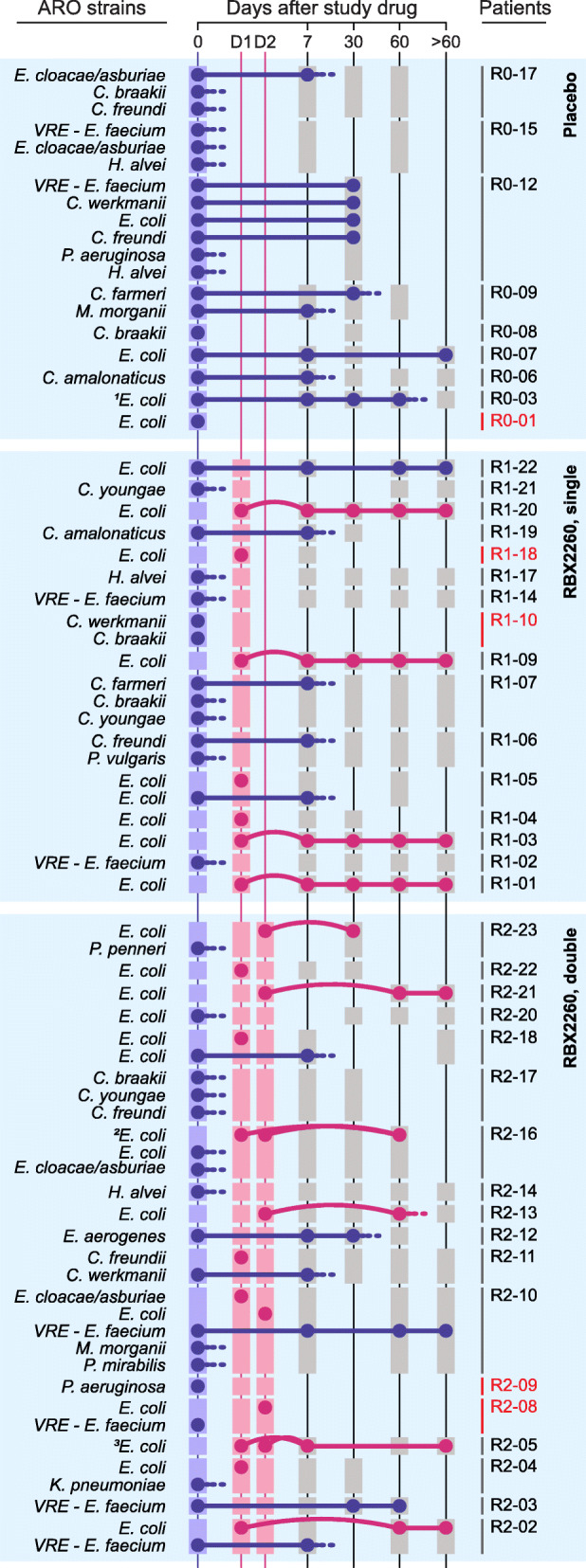
RBX2660 effectively cleared antibiotic-resistant organisms (AROs) compared to placebo and simultaneously introduced new AROs. We specifically tracked patient-derived (blue dot) and RBX2660-derived AROs (red dot). Patients with no ARO detected from both the baseline sample and corresponding RBX2660 were excluded. Persistency (solid line), disappearance (dash line), and introduction (curved line) of the AROs were determined by genomic comparison of AROs (the “ARO tracking and SNP calling” section). Squares indicate the sample availability (blue, patient baseline samples; red, RBX2660; gray, patient samples after RBX2660 administration). Patients with no samples after day 7 were marked with red. 1R0-03 showed 2–3 separate lineages of E. coli prior to day 30, which were reduced to 1 lineage by day 60. 2Patient R2-16 received the same RBX2660 product twice. 3Although the two RBX2660 products for patient R2-05 were prepared from different donor samples, ARO E. coli strains screened from those appeared to be clonal (distance = 8 SNPs)
