Figure 1: Novel Therapeutic Avenues with mTOR.
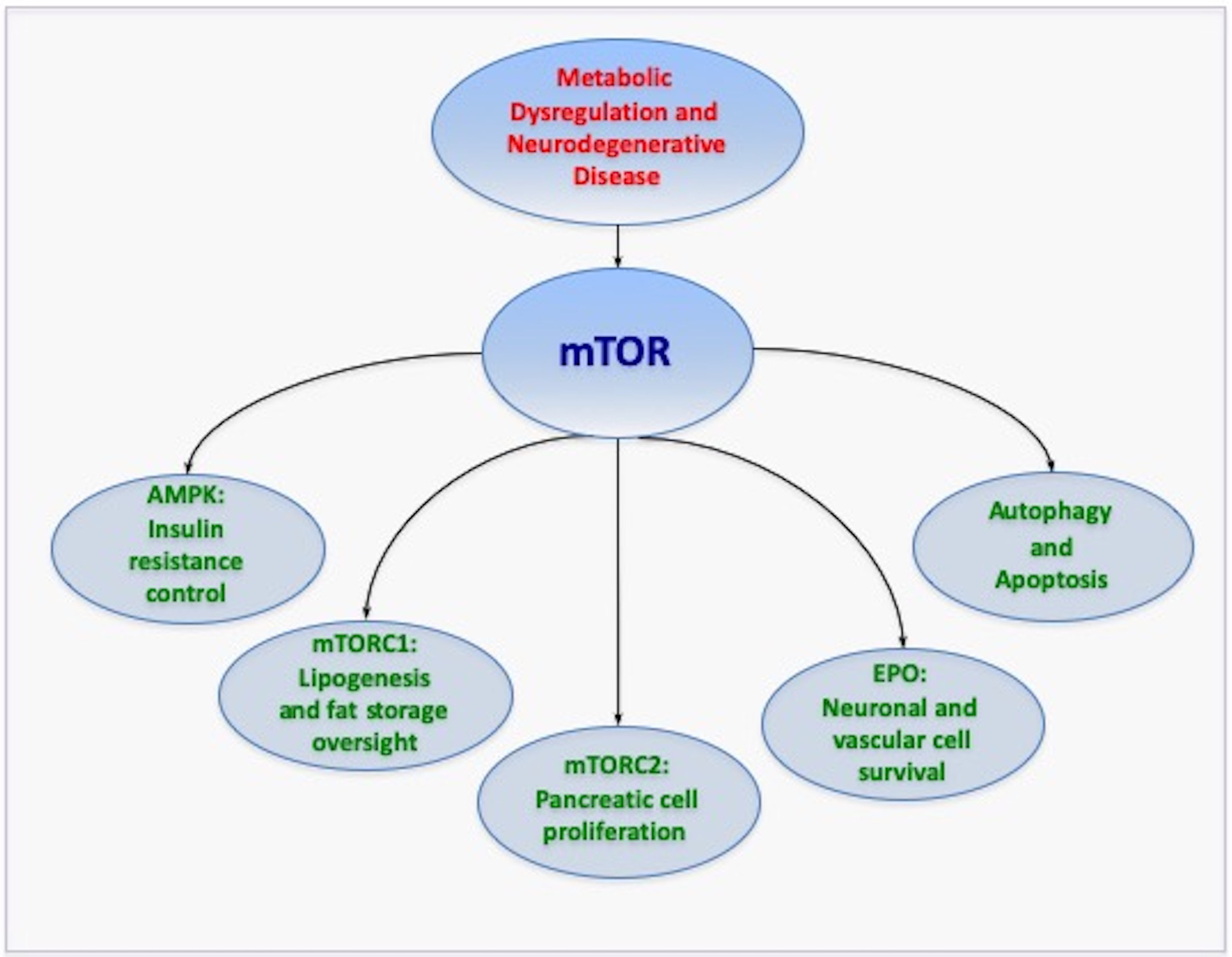
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) and its associated pathways of mTOR Complex 1 (mTORC1), mTOR Complex 2 (mTORC2), AMP activated protein kinase (AMPK), and the trophic factor erythropoietin offer novel therapeutic avenues to treat neurodegenerative disorders through metabolic pathways. mTOR and its pathways broadly impact metabolic disease and the nervous system through the oversight of programmed cell death pathways of autophagy and apoptosis. Given that current therapies for metabolic disease and neurodegenerative disorders address only symptomatic care, mTOR and its associated pathways provide strong prospects to treat both the onset and progression of metabolic disease in association with neurodegenerative disorders. Yet, it is clear that comprehensive understanding is required to appreciate the large breadth of mTOR pathways to safely translate treatments to clinical medicine without the onset of unexpected clinical disabilities.
